University of Houston Libraries
Nursing resources.
- About This Guide
- Scholarly Articles
- Books and eBooks
- Study Resources
- Data and Statistics
- Web Resources
- Health Assessment Videos
- Citation Resources
This page provides links to databases and journals where you can find articles and clinical information to help you with your research.

Recommended Resources
- Nursing & Allied Health Databases
Citation Indexes
Evidence-Based Practice Databases
Biomedicine Databases
- Dissertations & Theses Databases
Clinical Tools
Nursing & Allied Health Databases
- PubMed This link opens in a new window PubMed® comprises more than 30 million citations for biomedical literature from MEDLINE, life science journals, and online books.
- CINAHL Complete This link opens in a new window This database provides access to health science literature related to nursing and allied health disciplines. In addition, it includes standards of practice and evidence-based care guidelines.
- EMBASE This link opens in a new window EMBASE is a major biomedical and pharmaceutical database indexing over 3,500 international journals in the following fields: drug research, pharmacology, pharmaceutics, toxicology, clinical and experimental human medicine, health policy and management, public health, occupational health, environmental health, drug dependence and abuse, psychiatry, forensic medicine, and biomedical engineering/instrumentation. There is selective coverage for nursing, dentistry, veterinary medicine, psychology, and alternative medicine.
- Journals@Ovid This link opens in a new window The database aggregates hundreds of scientific, technical, and medical journals from over 50 publishers and societies, with each journal available by individual subscription. Includes access and searching of all the bibliographic citations, references, and abstracts in the database as well as to the full text of select journals.
- Ovid Nursing Database This link opens in a new window Exclusive collection of top nursing journals which are used by nurses, nursing students and health professionals around the world on a daily basis.
- See all nursing databases here.
Health science research is often multidisciplinary. Below is a list of multidisciplinary databases to start you in the right path. You can also use these databases to conduct basic searches to 'scope' out a subject; quickly find seminal articles; and conduct bibliometrics research.
Key Citation Indexes
- Web of Science This link opens in a new window Web of Science is a comprehensive research platform. Journal articles, patents, websites, conference proceedings, Open Access material—all can be accessed through one interface, using a variety of powerful search and analysis tools. Web of Science Core Collection is a painstakingly selected, actively curated database of the journals that researchers themselves have judged to be the most important and useful in their fields
Regional Indexes
- Global Index Medicus (GIM) Regional indexes for global health research provided by the World Health Organization. Consists of 5 regional indices (listed below) and contains literature published from low- and middle- income countries.
- African Index Medicus (AIM) International index to health information published in or related to Africa.
- LILACS: Latin American and Caribbean Health Sciences Literature Covers literature related to the health sciences and has been published in countries of Latin America and the Caribbean since 1982.
- Index Medicus for the Eastern Mediterranean Region (IMEMR) IMEMR comprises about 256,078 citations for health and biomedical sciences literature published in 782 peer-reviewed journals from 20 countries in the Region.
- Index Medicus for the South-East Asian Region (IMSEAR) IMSEAR is an archive of selected publications in health sciences in the WHO South-East Asia Region.
- Western Pacific Region Index Medicus (WPRIM) WPRIM is the regional bibliographic index of medical and health journals published by the Member States of the Western Pacific Region.
- PubMed Clinical Queries PubMed Clinical Queries allows you to quickly and easily search for relevant clinical literature on etiology, prognosis, diagnosis and therapy of diseases and diagnostics. PubMed Clinical Queries is designed to filter one search by three clinical research areas: Clinical Study Categories, Systematic Reviews, and Medical Genetics.
- MEDLINE with Full Text This link opens in a new window Full-text database providing access to top-tier biomedical and health journals.
Dissertations & Theses Databases
- DynaMed This link opens in a new window DynaMed is a clinical reference tool of more than 3000 topics designed for physicians and health care professionals for use primarily at the point-of-care. DynaMed is updated daily and monitors the content of over 500 medical journal and systemic evidence review databases.
- UpToDate This link opens in a new window A point-of-care clinical resource. Useful for quick information about conditions, drugs, etc.
Top Nursing Journals
Top 5 nursing journals with the highest 5-year impact factor rankings in Journal Citation Reports. If the full text is available from the UH Libraries, the title is in red (click to access).
- More Nursing Journals
What is a library database?
Your instructor or subject librarian may throw around the term "library database" a lot, but what exactly do they mean? This video from the University of Houston Libraries explains the term and how you can use databases for research.
Transcript available through YouTube .
Remote Access
You can access UH Libraries' online resources from anywhere!
To access online resources (e.g. databases, articles) while off campus, you will be asked to log in with your CourgarNet account . Once you log in, you will be redirected to the online resource you selected. You must be a current student, faculty, or staff.
If you do not know your CougarNet account information, then please contact UIT Support Center at:
713-743-1411
or chat with a support representative .
If you have any difficulties accessing UH Libraries' online resources, please use this form to let us know!
- << Previous: About This Guide
- Next: Books and eBooks >>

Health & Medicine Databases @ UH Libraries
Browse our best resources-organized by subject-available through UH Libraries. Databases are accessible to UH-affiliated users.
- Communication Sciences & Disorders Databases
- Health & Human Performance Databases
- Medicine Databases
- Nutrition Databases
- Pharmacy Databases
- Psychology Databases
- Social Work Databases
Search for Journals
Search by title or ISBN to see if UH Libraries has access to a particular journal. Journal search.
- Last Updated: Dec 13, 2024 9:22 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uh.edu/nursing
- Open access
- Published: 03 July 2024
The impact of evidence-based nursing leadership in healthcare settings: a mixed methods systematic review
- Maritta Välimäki 1 , 2 ,
- Shuang Hu 3 ,
- Tella Lantta 1 ,
- Kirsi Hipp 1 , 4 ,
- Jaakko Varpula 1 ,
- Jiarui Chen 3 ,
- Gaoming Liu 5 ,
- Yao Tang 3 ,
- Wenjun Chen 3 &
- Xianhong Li 3
BMC Nursing volume 23 , Article number: 452 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
13k Accesses
1 Citations
Metrics details
The central component in impactful healthcare decisions is evidence. Understanding how nurse leaders use evidence in their own managerial decision making is still limited. This mixed methods systematic review aimed to examine how evidence is used to solve leadership problems and to describe the measured and perceived effects of evidence-based leadership on nurse leaders and their performance, organizational, and clinical outcomes.
We included articles using any type of research design. We referred nurses, nurse managers or other nursing staff working in a healthcare context when they attempt to influence the behavior of individuals or a group in an organization using an evidence-based approach. Seven databases were searched until 11 November 2021. JBI Critical Appraisal Checklist for Quasi-experimental studies, JBI Critical Appraisal Checklist for Case Series, Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool were used to evaluate the Risk of bias in quasi-experimental studies, case series, mixed methods studies, respectively. The JBI approach to mixed methods systematic reviews was followed, and a parallel-results convergent approach to synthesis and integration was adopted.
Thirty-one publications were eligible for the analysis: case series ( n = 27), mixed methods studies ( n = 3) and quasi-experimental studies ( n = 1). All studies were included regardless of methodological quality. Leadership problems were related to the implementation of knowledge into practice, the quality of nursing care and the resource availability. Organizational data was used in 27 studies to understand leadership problems, scientific evidence from literature was sought in 26 studies, and stakeholders’ views were explored in 24 studies. Perceived and measured effects of evidence-based leadership focused on nurses’ performance, organizational outcomes, and clinical outcomes. Economic data were not available.
Conclusions
This is the first systematic review to examine how evidence is used to solve leadership problems and to describe its measured and perceived effects from different sites. Although a variety of perceptions and effects were identified on nurses’ performance as well as on organizational and clinical outcomes, available knowledge concerning evidence-based leadership is currently insufficient. Therefore, more high-quality research and clinical trial designs are still needed.
Trail registration
The study was registered (PROSPERO CRD42021259624).
Peer Review reports
Global health demands have set new roles for nurse leaders [ 1 ].Nurse leaders are referred to as nurses, nurse managers, or other nursing staff working in a healthcare context who attempt to influence the behavior of individuals or a group based on goals that are congruent with organizational goals [ 2 ]. They are seen as professionals “armed with data and evidence, and a commitment to mentorship and education”, and as a group in which “leaders innovate, transform, and achieve quality outcomes for patients, health care professionals, organizations, and communities” [ 3 ]. Effective leadership occurs when team members critically follow leaders and are motivated by a leader’s decisions based on the organization’s requests and targets [ 4 ]. On the other hand, problems caused by poor leadership may also occur, regarding staff relations, stress, sickness, or retention [ 5 ]. Therefore, leadership requires an understanding of different problems to be solved using synthesizing evidence from research, clinical expertise, and stakeholders’ preferences [ 6 , 7 ]. If based on evidence, leadership decisions, also referred as leadership decision making [ 8 ], could ensure adequate staffing [ 7 , 9 ] and to produce sufficient and cost-effective care [ 10 ]. However, nurse leaders still rely on their decision making on their personal [ 11 ] and professional experience [ 10 ] over research evidence, which can lead to deficiencies in the quality and safety of care delivery [ 12 , 13 , 14 ]. As all nurses should demonstrate leadership in their profession, their leadership competencies should be strengthened [ 15 ].
Evidence-informed decision-making, referred to as evidence appraisal and application, and evaluation of decisions [ 16 ], has been recognized as one of the core competencies for leaders [ 17 , 18 ]. The role of evidence in nurse leaders’ managerial decision making has been promoted by public authorities [ 19 , 20 , 21 ]. Evidence-based management, another concept related to evidence-based leadership, has been used as the potential to improve healthcare services [ 22 ]. It can guide nursing leaders, in developing working conditions, staff retention, implementation practices, strategic planning, patient care, and success of leadership [ 13 ]. Collins and Holton [ 23 ] in their systematic review and meta-analysis examined 83 studies regarding leadership development interventions. They found that leadership training can result in significant improvement in participants’ skills, especially in knowledge level, although the training effects varied across studies. Cummings et al. [ 24 ] reviewed 100 papers (93 studies) and concluded that participation in leadership interventions had a positive impact on the development of a variety of leadership styles. Clavijo-Chamorro et al. [ 25 ] in their review of 11 studies focused on leadership-related factors that facilitate evidence implementation: teamwork, organizational structures, and transformational leadership. The role of nurse managers was to facilitate evidence-based practices by transforming contexts to motivate the staff and move toward a shared vision of change.
As far as we are aware, however, only a few systematic reviews have focused on evidence-based leadership or related concepts in the healthcare context aiming to analyse how nurse leaders themselves uses evidence in the decision-making process. Young [ 26 ] targeted definitions and acceptance of evidence-based management (EBMgt) in healthcare while Hasanpoor et al. [ 22 ] identified facilitators and barriers, sources of evidence used, and the role of evidence in the process of decision making. Both these reviews concluded that EBMgt was of great importance but used limitedly in healthcare settings due to a lack of time, a lack of research management activities, and policy constraints. A review by Williams [ 27 ] showed that the usage of evidence to support management in decision making is marginal due to a shortage of relevant evidence. Fraser [ 28 ] in their review further indicated that the potential evidence-based knowledge is not used in decision making by leaders as effectively as it could be. Non-use of evidence occurs and leaders base their decisions mainly on single studies, real-world evidence, and experts’ opinions [ 29 ]. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses rarely provide evidence of management-related interventions [ 30 ]. Tate et al. [ 31 ] concluded based on their systematic review and meta-analysis that the ability of nurse leaders to use and critically appraise research evidence may influence the way policy is enacted and how resources and staff are used to meet certain objectives set by policy. This can further influence staff and workforce outcomes. It is therefore important that nurse leaders have the capacity and motivation to use the strongest evidence available to effect change and guide their decision making [ 27 ].
Despite of a growing body of evidence, we found only one review focusing on the impact of evidence-based knowledge. Geert et al. [ 32 ] reviewed literature from 2007 to 2016 to understand the elements of design, delivery, and evaluation of leadership development interventions that are the most reliably linked to outcomes at the level of the individual and the organization, and that are of most benefit to patients. The authors concluded that it is possible to improve individual-level outcomes among leaders, such as knowledge, motivation, skills, and behavior change using evidence-based approaches. Some of the most effective interventions included, for example, interactive workshops, coaching, action learning, and mentoring. However, these authors found limited research evidence describing how nurse leaders themselves use evidence to support their managerial decisions in nursing and what the outcomes are.
To fill the knowledge gap and compliment to existing knowledgebase, in this mixed methods review we aimed to (1) examine what leadership problems nurse leaders solve using an evidence-based approach and (2) how they use evidence to solve these problems. We also explored (3) the measured and (4) perceived effects of the evidence-based leadership approach in healthcare settings. Both qualitative and quantitative components of the effects of evidence-based leadership were examined to provide greater insights into the available literature [ 33 ]. Together with the evidence-based leadership approach, and its impact on nursing [ 34 , 35 ], this knowledge gained in this review can be used to inform clinical policy or organizational decisions [ 33 ]. The study is registered (PROSPERO CRD42021259624). The methods used in this review were specified in advance and documented in a priori in a published protocol [ 36 ]. Key terms of the review and the search terms are defined in Table 1 (population, intervention, comparison, outcomes, context, other).
In this review, we used a mixed methods approach [ 37 ]. A mixed methods systematic review was selected as this approach has the potential to produce direct relevance to policy makers and practitioners [ 38 ]. Johnson and Onwuegbuzie [ 39 ] have defined mixed methods research as “the class of research in which the researcher mixes or combines quantitative and qualitative research techniques, methods, approaches, concepts or language into a single study.” Therefore, we combined quantitative and narrative analysis to appraise and synthesize empirical evidence, and we held them as equally important in informing clinical policy or organizational decisions [ 34 ]. In this review, a comprehensive synthesis of quantitative and qualitative data was performed first and then discussed in discussion part (parallel-results convergent design) [ 40 ]. We hoped that different type of analysis approaches could complement each other and deeper picture of the topic in line with our research questions could be gained [ 34 ].
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusion and exclusion criteria of the study are described in Table 1 .
Search strategy
A three-step search strategy was utilized. First, an initial limited search with #MEDLINE was undertaken, followed by analysis of the words used in the title, abstract, and the article’s key index terms. Second, the search strategy, including identified keywords and index terms, was adapted for each included data base and a second search was undertaken on 11 November 2021. The full search strategy for each database is described in Additional file 1 . Third, the reference list of all studies included in the review were screened for additional studies. No year limits or language restrictions were used.
Information sources
The database search included the following: CINAHL (EBSCO), Cochrane Library (academic database for medicine and health science and nursing), Embase (Elsevier), PsycINFO (EBSCO), PubMed (MEDLINE), Scopus (Elsevier) and Web of Science (academic database across all scientific and technical disciplines, ranging from medicine and social sciences to arts and humanities). These databases were selected as they represent typical databases in health care context. Subject headings from each of the databases were included in the search strategies. Boolean operators ‘AND’ and ‘OR’ were used to combine the search terms. An information specialist from the University of Turku Library was consulted in the formation of the search strategies.
Study selection
All identified citations were collated and uploaded into Covidence software (Covidence systematic review software, Veritas Health Innovation, Melbourne, Australia www.covidence.org ), and duplicates were removed by the software. Titles and abstracts were screened and assessed against the inclusion criteria independently by two reviewers out of four, and any discrepancies were resolved by the third reviewer (MV, KH, TL, WC). Studies meeting the inclusion criteria were retrieved in full and archived in Covidence. Access to one full-text article was lacking: the authors for one study were contacted about the missing full text, but no full text was received. All remaining hits of the included studies were retrieved and assessed independently against the inclusion criteria by two independent reviewers of four (MV, KH, TL, WC). Studies that did not meet the inclusion criteria were excluded, and the reasons for exclusion were recorded in Covidence. Any disagreements that arose between the reviewers were resolved through discussions with XL.
Assessment of methodological quality
Eligible studies were critically appraised by two independent reviewers (YT, SH). Standardized critical appraisal instruments based on the study design were used. First, quasi-experimental studies were assessed using the JBI Critical Appraisal Checklist for Quasi-experimental studies [ 44 ]. Second, case series were assessed using the JBI Critical Appraisal Checklist for Case Series [ 45 ]. Third, mixed methods studies were appraised using the Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool [ 46 ].
To increase inter-reviewer reliability, the review agreement was calculated (SH) [ 47 ]. A kappa greater than 0.8 was considered to represent a high level of agreement (0–0.1). In our data, the agreement was 0.75. Discrepancies raised between two reviewers were resolved through discussion and modifications and confirmed by XL. As an outcome, studies that met the inclusion criteria were proceeded to critical appraisal and assessed as suitable for inclusion in the review. The scores for each item and overall critical appraisal scores were presented.
Data extraction
For data extraction, specific tables were created. First, study characteristics (author(s), year, country, design, number of participants, setting) were extracted by two authors independently (JC, MV) and reviewed by TL. Second, descriptions of the interventions were extracted by two reviewers (JV, JC) using the structure of the TIDIeR (Template for Intervention Description and Replication) checklist (brief name, the goal of the intervention, material and procedure, models of delivery and location, dose, modification, adherence and fidelity) [ 48 ]. The extractions were confirmed (MV).
Third, due to a lack of effectiveness data and a wide heterogeneity between study designs and presentation of outcomes, no attempt was made to pool the quantitative data statistically; the findings of the quantitative data were presented in narrative form only [ 44 ]. The separate data extraction tables for each research question were designed specifically for this study. For both qualitative (and a qualitative component of mixed-method studies) and quantitative studies, the data were extracted and tabulated into text format according to preplanned research questions [ 36 ]. To test the quality of the tables and the data extraction process, three authors independently extracted the data from the first five studies (in alphabetical order). After that, the authors came together to share and determine whether their approaches of the data extraction were consistent with each other’s output and whether the content of each table was in line with research question. No reason was found to modify the data extraction tables or planned process. After a consensus of the data extraction process was reached, the data were extracted in pairs by independent reviewers (WC, TY, SH, GL). Any disagreements that arose between the reviewers were resolved through discussion and with a third reviewer (MV).
Data analysis
We were not able to conduct a meta-analysis due to a lack of effectiveness data based on clinical trials. Instead, we used inductive thematic analysis with constant comparison to answer the research question [ 46 , 49 ] using tabulated primary data from qualitative and quantitative studies as reported by the original authors in narrative form only [ 47 ]. In addition, the qualitizing process was used to transform quantitative data to qualitative data; this helped us to convert the whole data into themes and categories. After that we used the thematic analysis for the narrative data as follows. First, the text was carefully read, line by line, to reveal topics answering each specific review question (MV). Second, the data coding was conducted, and the themes in the data were formed by data categorization. The process of deriving the themes was inductive based on constant comparison [ 49 ]. The results of thematic analysis and data categorization was first described in narrative format and then the total number of studies was calculated where the specific category was identified (%).
Stakeholder involvement
The method of reporting stakeholders’ involvement follows the key components by [ 50 ]: (1) people involved, (2) geographical location, (3) how people were recruited, (4) format of involvement, (5) amount of involvement, (6) ethical approval, (7) financial compensation, and (8) methods for reporting involvement.
In our review, stakeholder involvement targeted nurses and nurse leader in China. Nurse Directors of two hospitals recommended potential participants who received a personal invitation letter from researchers to participate in a discussion meeting. Stakeholders’ participation was based on their own free will. Due to COVID-19, one online meeting (1 h) was organized (25 May 2022). Eleven participants joined the meeting. Ethical approval was not applied and no financial compensation was offered. At the end of the meeting, experiences of stakeholders’ involvement were explored.
The meeting started with an introductory presentation with power points. The rationale, methods, and preliminary review results were shared with the participants [ 51 ].The meeting continued with general questions for the participants: (1) Are you aware of the concepts of evidence-based practice or evidence-based leadership?; (2) How important is it to use evidence to support decisions among nurse leaders?; (3) How is the evidence-based approach used in hospital settings?; and (4) What type of evidence is currently used to support nurse leaders’ decision making (e.g. scientific literature, organizational data, stakeholder views)?
Two people took notes on the course and content of the conversation. The notes were later transcripted in verbatim, and the key points of the discussions were summarised. Although answers offered by the stakeholders were very short, the information was useful to validate the preliminary content of the results, add the rigorousness of the review, and obtain additional perspectives. A recommendation of the stakeholders was combined in the Discussion part of this review increasing the applicability of the review in the real world [ 50 ]. At the end of the discussion, the value of stakeholders’ involvement was asked. Participants shared that the experience of participating was unique and the topic of discussion was challenging. Two authors of the review group further represented stakeholders by working together with the research team throughout the review study.
Search results
From seven different electronic databases, 6053 citations were identified as being potentially relevant to the review. Then, 3133 duplicates were removed by an automation tool (Covidence: www.covidence.org ), and one was removed manually. The titles and abstracts of 3040 of citations were reviewed, and a total of 110 full texts were included (one extra citation was found on the reference list but later excluded). Based on the eligibility criteria, 31 studies (32 hits) were critically appraised and deemed suitable for inclusion in the review. The search results and selection process are presented in the PRISMA [ 52 ] flow diagram Fig. 1 . The full list of references for included studies can be find in Additional file 2 . To avoid confusion between articles of the reference list and studies included in the analysis, the studies included in the review are referred inside the article using the reference number of each study (e.g. ref 1, ref 2).
Search results and study selection and inclusion process [ 52 ]
Characteristics of included studies
The studies had multiple purposes, aiming to develop practice, implement a new approach, improve quality, or to develop a model. The 31 studies (across 32 hits) were case series studies ( n = 27), mixed methods studies ( n = 3) and a quasi-experimental study ( n = 1). All studies were published between the years 2004 and 2021. The highest number of papers was published in year 2020.
Table 2 describes the characteristics of included studies and Additional file 3 offers a narrative description of the studies.
Methodological quality assessment
Quasi-experimental studies.
We had one quasi-experimental study (ref 31). All questions in the critical appraisal tool were applicable. The total score of the study was 8 (out of a possible 9). Only one response of the tool was ‘no’ because no control group was used in the study (see Additional file 4 for the critical appraisal of included studies).
Case series studies . A case series study is typically defined as a collection of subjects with common characteristics. The studies do not include a comparison group and are often based on prevalent cases and on a sample of convenience [ 53 ]. Munn et al. [ 45 ] further claim that case series are best described as observational studies, lacking experimental and randomized characteristics, being descriptive studies, without a control or comparator group. Out of 27 case series studies included in our review, the critical appraisal scores varied from 1 to 9. Five references were conference abstracts with empirical study results, which were scored from 1 to 3. Full reports of these studies were searched in electronic databases but not found. Critical appraisal scores for the remaining 22 studies ranged from 1 to 9 out of a possible score of 10. One question (Q3) was not applicable to 13 studies: “Were valid methods used for identification of the condition for all participants included in the case series?” Only two studies had clearly reported the demographic of the participants in the study (Q6). Twenty studies met Criteria 8 (“Were the outcomes or follow-up results of cases clearly reported?”) and 18 studies met Criteria 7 (“Q7: Was there clear reporting of clinical information of the participants?”) (see Additional file 4 for the critical appraisal of included studies).
Mixed-methods studies
Mixed-methods studies involve a combination of qualitative and quantitative methods. This is a common design and includes convergent design, sequential explanatory design, and sequential exploratory design [ 46 ]. There were three mixed-methods studies. The critical appraisal scores for the three studies ranged from 60 to 100% out of a possible 100%. Two studies met all the criteria, while one study fulfilled 60% of the scored criteria due to a lack of information to understand the relevance of the sampling strategy well enough to address the research question (Q4.1) or to determine whether the risk of nonresponse bias was low (Q4.4) (see Additional file 4 for the critical appraisal of included studies).
Intervention or program components
The intervention of program components were categorized and described using the TiDier checklist: name and goal, theory or background, material, procedure, provider, models of delivery, location, dose, modification, and adherence and fidelity [ 48 ]. A description of intervention in each study is described in Additional file 5 and a narrative description in Additional file 6 .
Leadership problems
In line with the inclusion criteria, data for the leadership problems were categorized in all 31 included studies (see Additional file 7 for leadership problems). Three types of leadership problems were identified: implementation of knowledge into practice, the quality of clinical care, and resources in nursing care. A narrative summary of the results is reported below.
Implementing knowledge into practice
Eleven studies (35%) aimed to solve leadership problems related to implementation of knowledge into practice. Studies showed how to support nurses in evidence-based implementation (EBP) (ref 3, ref 5), how to engage nurses in using evidence in practice (ref 4), how to convey the importance of EBP (ref 22) or how to change practice (ref 4). Other problems were how to facilitate nurses to use guideline recommendations (ref 7) and how nurses can make evidence-informed decisions (ref 8). General concerns also included the linkage between theory and practice (ref 1) as well as how to implement the EBP model in practice (ref 6). In addition, studies were motivated by the need for revisions or updates of protocols to improve clinical practice (ref 10) as well as the need to standardize nursing activities (ref 11, ref 14).
The quality of the care
Thirteen (42%) focused on solving problems related to the quality of clinical care. In these studies, a high number of catheter infections led a lack of achievement of organizational goals (ref 2, ref 9). A need to reduce patient symptoms in stem cell transplant patients undergoing high-dose chemotherapy (ref 24) was also one of the problems to be solved. In addition, the projects focused on how to prevent pressure ulcers (ref 26, ref 29), how to enhance the quality of cancer treatment (ref 25) and how to reduce the need for invasive constipation treatment (ref 30). Concerns about patient safety (ref 15), high fall rates (ref 16, ref 19), dissatisfaction of patients (ref 16, ref 18) and nurses (ref 16, ref 30) were also problems that had initiated the projects. Studies addressed concerns about how to promote good contingency care in residential aged care homes (ref 20) and about how to increase recognition of human trafficking problems in healthcare (ref 21).
Resources in nursing care
Nurse leaders identified problems in their resources, especially in staffing problems. These problems were identified in seven studies (23%), which involved concerns about how to prevent nurses from leaving the job (ref 31), how to ensure appropriate recruitment, staffing and retaining of nurses (ref 13) and how to decrease nurses’ burden and time spent on nursing activities (ref 12). Leadership turnover was also reported as a source of dissatisfaction (ref 17); studies addressed a lack of structured transition and training programs, which led to turnover (ref 23), as well as how to improve intershift handoff among nurses (ref 28). Optimal design for new hospitals was also examined (ref 27).
Main features of evidence-based leadership
Out of 31 studies, 17 (55%) included all four domains of an evidence-based leadership approach, and four studies (13%) included evidence of critical appraisal of the results (see Additional file 8 for the main features of evidence-based Leadership) (ref 11, ref 14, ref 23, ref 27).
Organizational evidence
Twenty-seven studies (87%) reported how organizational evidence was collected and used to solve leadership problems (ref 2). Retrospective chart reviews (ref 5), a review of the extent of specific incidents (ref 19), and chart auditing (ref 7, ref 25) were conducted. A gap between guideline recommendations and actual care was identified using organizational data (ref 7) while the percentage of nurses’ working time spent on patient care was analyzed using an electronic charting system (ref 12). Internal data (ref 22), institutional data, and programming metrics were also analyzed to understand the development of the nurse workforce (ref 13).
Surveys (ref 3, ref 25), interviews (ref 3, ref 25) and group reviews (ref 18) were used to better understand the leadership problem to be solved. Employee opinion surveys on leadership (ref 17), a nurse satisfaction survey (ref 30) and a variety of reporting templates were used for the data collection (ref 28) reported. Sometimes, leadership problems were identified by evidence facilitators or a PI’s team who worked with staff members (ref 15, ref 17). Problems in clinical practice were also identified by the Nursing Professional Council (ref 14), managers (ref 26) or nurses themselves (ref 24). Current practices were reviewed (ref 29) and a gap analysis was conducted (ref 4, ref 16, ref 23) together with SWOT analysis (ref 16). In addition, hospital mission and vision statements, research culture established and the proportion of nursing alumni with formal EBP training were analyzed (ref 5). On the other hand, it was stated that no systematic hospital-specific sources of data regarding job satisfaction or organizational commitment were used (ref 31). In addition, statements of organizational analysis were used on a general level only (ref 1).
Scientific evidence identified
Twenty-six studies (84%) reported the use of scientific evidence in their evidence-based leadership processes. A literature search was conducted (ref 21) and questions, PICO, and keywords were identified (ref 4) in collaboration with a librarian. Electronic databases, including PubMed (ref 14, ref 31), Cochrane, and EMBASE (ref 31) were searched. Galiano (ref 6) used Wiley Online Library, Elsevier, CINAHL, Health Source: Nursing/Academic Edition, PubMed, and the Cochrane Library while Hoke (ref 11) conducted an electronic search using CINAHL and PubMed to retrieve articles.
Identified journals were reviewed manually (ref 31). The findings were summarized using ‘elevator speech’ (ref 4). In a study by Gifford et al. (ref 9) evidence facilitators worked with participants to access, appraise, and adapt the research evidence to the organizational context. Ostaszkiewicz (ref 20) conducted a scoping review of literature and identified and reviewed frameworks and policy documents about the topic and the quality standards. Further, a team of nursing administrators, directors, staff nurses, and a patient representative reviewed the literature and made recommendations for practice changes.
Clinical practice guidelines were also used to offer scientific evidence (ref 7, ref 19). Evidence was further retrieved from a combination of nursing policies, guidelines, journal articles, and textbooks (ref 12) as well as from published guidelines and literature (ref 13). Internal evidence, professional practice knowledge, relevant theories and models were synthesized (ref 24) while other study (ref 25) reviewed individual studies, synthesized with systematic reviews or clinical practice guidelines. The team reviewed the research evidence (ref 3, ref 15) or conducted a literature review (ref 22, ref 28, ref 29), a literature search (ref 27), a systematic review (ref 23), a review of the literature (ref 30) or ‘the scholarly literature was reviewed’ (ref 18). In addition, ‘an extensive literature review of evidence-based best practices was carried out’ (ref 10). However, detailed description how the review was conducted was lacking.
Views of stakeholders
A total of 24 studies (77%) reported methods for how the views of stakeholders, i.e., professionals or experts, were considered. Support to run this study was received from nursing leadership and multidisciplinary teams (ref 29). Experts and stakeholders joined the study team in some cases (ref 25, ref 30), and in other studies, their opinions were sought to facilitate project success (ref 3). Sometimes a steering committee was formed by a Chief Nursing Officer and Clinical Practice Specialists (ref 2). More specifically, stakeholders’ views were considered using interviews, workshops and follow-up teleconferences (ref 7). The literature review was discussed with colleagues (ref 11), and feedback and support from physicians as well as the consensus of staff were sought (ref 16).
A summary of the project findings and suggestions for the studies were discussed at 90-minute weekly meetings by 11 charge nurses. Nurse executive directors were consulted over a 10-week period (ref 31). An implementation team (nurse, dietician, physiotherapist, occupational therapist) was formed to support the implementation of evidence-based prevention measures (ref 26). Stakeholders volunteered to join in the pilot implementation (ref 28) or a stakeholder team met to determine the best strategy for change management, shortcomings in evidence-based criteria were discussed, and strategies to address those areas were planned (ref 5). Nursing leaders, staff members (ref 22), ‘process owners (ref 18) and program team members (ref 18, ref 19, ref 24) met regularly to discuss the problems. Critical input was sought from clinical educators, physicians, nutritionists, pharmacists, and nurse managers (ref 24). The unit director and senior nursing staff reviewed the contents of the product, and the final version of clinical pathways were reviewed and approved by the Quality Control Commission of the Nursing Department (ref 12). In addition, two co-design workshops with 18 residential aged care stakeholders were organized to explore their perspectives about factors to include in a model prototype (ref 20). Further, an agreement of stakeholders in implementing continuous quality services within an open relationship was conducted (ref 1).
Critical appraisal
In five studies (16%), a critical appraisal targeting the literature search was carried out. The appraisals were conducted by interns and teams who critiqued the evidence (ref 4). In Hoke’s study, four areas that had emerged in the literature were critically reviewed (ref 11). Other methods were to ‘critically appraise the search results’ (ref 14). Journal club team meetings (ref 23) were organized to grade the level and quality of evidence and the team ‘critically appraised relevant evidence’ (ref 27). On the other hand, the studies lacked details of how the appraisals were done in each study.
The perceived effects of evidence-based leadership
Perceived effects of evidence-based leadership on nurses’ performance.
Eleven studies (35%) described perceived effects of evidence-based leadership on nurses’ performance (see Additional file 9 for perceived effects of evidence-based leadership), which were categorized in four groups: awareness and knowledge, competence, ability to understand patients’ needs, and engagement. First, regarding ‘awareness and knowledge’, different projects provided nurses with new learning opportunities (ref 3). Staff’s knowledge (ref 20, ref 28), skills, and education levels improved (ref 20), as did nurses’ knowledge comprehension (ref 21). Second, interventions and approaches focusing on management and leadership positively influenced participants’ competence level to improve the quality of services. Their confidence level (ref 1) and motivation to change practice increased, self-esteem improved, and they were more positive and enthusiastic in their work (ref 22). Third, some nurses were relieved that they had learned to better handle patients’ needs (ref 25). For example, a systematic work approach increased nurses’ awareness of the patients who were at risk of developing health problems (ref 26). And last, nurse leaders were more engaged with staff, encouraging them to adopt the new practices and recognizing their efforts to change (ref 8).
Perceived effects on organizational outcomes
Nine studies (29%) described the perceived effects of evidence-based leadership on organizational outcomes (see Additional file 9 for perceived effects of evidence-based leadership). These were categorized into three groups: use of resources, staff commitment, and team effort. First, more appropriate use of resources was reported (ref 15, ref 20), and working time was more efficiently used (ref 16). In generally, a structured approach made implementing change more manageable (ref 1). On the other hand, in the beginning of the change process, the feedback from nurses was unfavorable, and they experienced discomfort in the new work style (ref 29). New approaches were also perceived as time consuming (ref 3). Second, nurse leaders believed that fewer nursing staff than expected left the organization over the course of the study (ref 31). Third, the project helped staff in their efforts to make changes, and it validated the importance of working as a team (ref 7). Collaboration and support between the nurses increased (ref 26). On the other hand, new work style caused challenges in teamwork (ref 3).
Perceived effects on clinical outcomes
Five studies (16%) reported the perceived effects of evidence-based leadership on clinical outcomes (see Additional file 9 for perceived effects of evidence-based leadership), which were categorized in two groups: general patient outcomes and specific clinical outcomes. First, in general, the project assisted in connecting the guideline recommendations and patient outcomes (ref 7). The project was good for the patients in general, and especially to improve patient safety (ref 16). On the other hand, some nurses thought that the new working style did not work at all for patients (ref 28). Second, the new approach used assisted in optimizing patients’ clinical problems and person-centered care (ref 20). Bowel management, for example, received very good feedback (ref 30).
The measured effects of evidence-based leadership
The measured effects on nurses’ performance.
Data were obtained from 20 studies (65%) (see Additional file 10 for measured effects of evidence-based leadership) and categorized nurse performance outcomes for three groups: awareness and knowledge, engagement, and satisfaction. First, six studies (19%) measured the awareness and knowledge levels of participants. Internship for staff nurses was beneficial to help participants to understand the process for using evidence-based practice and to grow professionally, to stimulate for innovative thinking, to give knowledge needed to use evidence-based practice to answer clinical questions, and to make possible to complete an evidence-based practice project (ref 3). Regarding implementation program of evidence-based practice, those with formal EBP training showed an improvement in knowledge, attitude, confidence, awareness and application after intervention (ref 3, ref 11, ref 20, ref 23, ref 25). On the contrary, in other study, attitude towards EBP remained stable ( p = 0.543). and those who applied EBP decreased although no significant differences over the years ( p = 0.879) (ref 6).
Second, 10 studies (35%) described nurses’ engagement to new practices (ref 5, ref 6, ref 7, ref 10, ref 16, ref 17, ref 18, ref 21, ref 25, ref 27). 9 studies (29%) studies reported that there was an improvement of compliance level of participants (ref 6, ref 7, ref 10, ref 16, ref 17, ref 18, ref 21, ref 25, ref 27). On the contrary, in DeLeskey’s (ref 5) study, although improvement was found in post-operative nausea and vomiting’s (PONV) risk factors documented’ (2.5–63%), and ’risk factors communicated among anaesthesia and surgical staff’ (0–62%), the improvement did not achieve the goal. The reason was a limited improvement was analysed. It was noted that only those patients who had been seen by the pre-admission testing nurse had risk assessments completed. Appropriate treatment/prophylaxis increased from 69 to 77%, and from 30 to 49%; routine assessment for PONV/rescue treatment 97% and 100% was both at 100% following the project. The results were discussed with staff but further reasons for a lack of engagement in nursing care was not reported.
And third, six studies (19%) reported nurses’ satisfaction with project outcomes. The study results showed that using evidence in managerial decisions improved nurses’ satisfaction and attitudes toward their organization ( P < 0.05) (ref 31). Nurses’ overall job satisfaction improved as well (ref 17). Nurses’ satisfaction with usability of the electronic charting system significantly improved after introduction of the intervention (ref 12). In handoff project in seven hospitals, improvement was reported in all satisfaction indicators used in the study although improvement level varied in different units (ref 28). In addition, positive changes were reported in nurses’ ability to autonomously perform their job (“How satisfied are you with the tools and resources available for you treat and prevent patient constipation?” (54%, n = 17 vs. 92%, n = 35, p < 0.001) (ref 30).
The measured effects on organizational outcomes
Thirteen studies (42%) described the effects of a project on organizational outcomes (see Additional file 10 for measured effects of evidence-based leadership), which were categorized in two groups: staff compliance, and changes in practices. First, studies reported improved organizational outcomes due to staff better compliance in care (ref 4, ref 13, ref 17, ref 23, ref 27, ref 31). Second, changes in organization practices were also described (ref 11) like changes in patient documentation (ref 12, ref 21). Van Orne (ref 30) found a statistically significant reduction in the average rate of invasive medication administration between pre-intervention and post-intervention ( p = 0.01). Salvador (ref 24) also reported an improvement in a proactive approach to mucositis prevention with an evidence-based oral care guide. On the contrary, concerns were also raised such as not enough time for new bedside report (ref 16) or a lack of improvement of assessment of diabetic ulcer (ref 8).
The measured effects on clinical outcomes
A variety of improvements in clinical outcomes were reported (see Additional file 10 for measured effects of evidence-based leadership): improvement in patient clinical status and satisfaction level. First, a variety of improvement in patient clinical status was reported. improvement in Incidence of CAUTI decreased 27.8% between 2015 and 2019 (ref 2) while a patient-centered quality improvement project reduced CAUTI rates to 0 (ref 10). A significant decrease in transmission rate of MRSA transmission was also reported (ref 27) and in other study incidences of CLABSIs dropped following of CHG bathing (ref 14). Further, it was possible to decrease patient nausea from 18 to 5% and vomiting to 0% (ref 5) while the percentage of patients who left the hospital without being seen was below 2% after the project (ref 17). In addition, a significant reduction in the prevalence of pressure ulcers was found (ref 26, ref 29) and a significant reduction of mucositis severity/distress was achieved (ref 24). Patient falls rate decreased (ref 15, ref 16, ref 19, ref 27).
Second, patient satisfaction level after project implementation improved (ref 28). The scale assessing healthcare providers by consumers showed improvement, but the changes were not statistically significant. Improvement in an emergency department leadership model and in methods of communication with patients improved patient satisfaction scores by 600% (ref 17). In addition, new evidence-based unit improved patient experiences about the unit although not all items improved significantly (ref 18).
Stakeholder involvement in the mixed-method review
To ensure stakeholders’ involvement in the review, the real-world relevance of our research [ 53 ], achieve a higher level of meaning in our review results, and gain new perspectives on our preliminary findings [ 50 ], a meeting with 11 stakeholders was organized. First, we asked if participants were aware of the concepts of evidence-based practice or evidence-based leadership. Responses revealed that participants were familiar with the concept of evidence-based practice, but the topic of evidence-based leadership was totally new. Examples of nurses and nurse leaders’ responses are as follows: “I have heard a concept of evidence-based practice but never a concept of evidence-based leadership.” Another participant described: “I have heard it [evidence-based leadership] but I do not understand what it means.”
Second, as stakeholder involvement is beneficial to the relevance and impact of health research [ 54 ], we asked how important evidence is to them in supporting decisions in health care services. One participant described as follows: “Using evidence in decisions is crucial to the wards and also to the entire hospital.” Third, we asked how the evidence-based approach is used in hospital settings. Participants expressed that literature is commonly used to solve clinical problems in patient care but not to solve leadership problems. “In [patient] medication and care, clinical guidelines are regularly used. However, I am aware only a few cases where evidence has been sought to solve leadership problems.”
And last, we asked what type of evidence is currently used to support nurse leaders’ decision making (e.g. scientific literature, organizational data, stakeholder views)? The participants were aware that different types of information were collected in their organization on a daily basis (e.g. patient satisfaction surveys). However, the information was seldom used to support decision making because nurse leaders did not know how to access this information. Even so, the participants agreed that the use of evidence from different sources was important in approaching any leadership or managerial problems in the organization. Participants also suggested that all nurse leaders should receive systematic training related to the topic; this could support the daily use of the evidence-based approach.
To our knowledge, this article represents the first mixed-methods systematic review to examine leadership problems, how evidence is used to solve these problems and what the perceived and measured effects of evidence-based leadership are on nurse leaders and their performance, organizational, and clinical outcomes. This review has two key findings. First, the available research data suggests that evidence-based leadership has potential in the healthcare context, not only to improve knowledge and skills among nurses, but also to improve organizational outcomes and the quality of patient care. Second, remarkably little published research was found to explore the effects of evidence-based leadership with an efficient trial design. We validated the preliminary results with nurse stakeholders, and confirmed that nursing staff, especially nurse leaders, were not familiar with the concept of evidence-based leadership, nor were they used to implementing evidence into their leadership decisions. Our data was based on many databases, and we screened a large number of studies. We also checked existing registers and databases and found no registered or ongoing similar reviews being conducted. Therefore, our results may not change in the near future.
We found that after identifying the leadership problems, 26 (84%) studies out of 31 used organizational data, 25 (81%) studies used scientific evidence from the literature, and 21 (68%) studies considered the views of stakeholders in attempting to understand specific leadership problems more deeply. However, only four studies critically appraised any of these findings. Considering previous critical statements of nurse leaders’ use of evidence in their decision making [ 14 , 30 , 31 , 34 , 55 ], our results are still quite promising.
Our results support a previous systematic review by Geert et al. [ 32 ], which concluded that it is possible to improve leaders’ individual-level outcomes, such as knowledge, motivation, skills, and behavior change using evidence-based approaches. Collins and Holton [ 23 ] particularly found that leadership training resulted in significant knowledge and skill improvements, although the effects varied widely across studies. In our study, evidence-based leadership was seen to enable changes in clinical practice, especially in patient care. On the other hand, we understand that not all efforts to changes were successful [ 56 , 57 , 58 ]. An evidence-based approach causes negative attitudes and feelings. Negative emotions in participants have also been reported due to changes, such as discomfort with a new working style [ 59 ]. Another study reported inconvenience in using a new intervention and its potential risks for patient confidentiality. Sometimes making changes is more time consuming than continuing with current practice [ 60 ]. These findings may partially explain why new interventions or program do not always fully achieve their goals. On the other hand, Dubose et al. [ 61 ] state that, if prepared with knowledge of resistance, nurse leaders could minimize the potential negative consequences and capitalize on a powerful impact of change adaptation.
We found that only six studies used a specific model or theory to understand the mechanism of change that could guide leadership practices. Participants’ reactions to new approaches may be an important factor in predicting how a new intervention will be implemented into clinical practice. Therefore, stronger effort should be put to better understanding the use of evidence, how participants’ reactions and emotions or practice changes could be predicted or supported using appropriate models or theories, and how using these models are linked with leadership outcomes. In this task, nurse leaders have an important role. At the same time, more responsibilities in developing health services have been put on the shoulders of nurse leaders who may already be suffering under pressure and increased burden at work. Working in a leadership position may also lead to role conflict. A study by Lalleman et al. [ 62 ] found that nurses were used to helping other people, often in ad hoc situations. The helping attitude of nurses combined with structured managerial role may cause dilemmas, which may lead to stress. Many nurse leaders opt to leave their positions less than 5 years [ 63 ].To better fulfill the requirements of health services in the future, the role of nurse leaders in evidence-based leadership needs to be developed further to avoid ethical and practical dilemmas in their leadership practices.
It is worth noting that the perceived and measured effects did not offer strong support to each other but rather opened a new venue to understand the evidence-based leadership. Specifically, the perceived effects did not support to measured effects (competence, ability to understand patients’ needs, use of resources, team effort, and specific clinical outcomes) while the measured effects could not support to perceived effects (nurse’s performance satisfaction, changes in practices, and clinical outcomes satisfaction). These findings may indicate that different outcomes appear if the effects of evidence-based leadership are looked at using different methodological approach. Future study is encouraged using well-designed study method including mixed-method study to examine the consistency between perceived and measured effects of evidence-based leadership in health care.
There is a potential in nursing to support change by demonstrating conceptual and operational commitment to research-based practices [ 64 ]. Nurse leaders are well positioned to influence and lead professional governance, quality improvement, service transformation, change and shared governance [ 65 ]. In this task, evidence-based leadership could be a key in solving deficiencies in the quality, safety of care [ 14 ] and inefficiencies in healthcare delivery [ 12 , 13 ]. As WHO has revealed, there are about 28 million nurses worldwide, and the demand of nurses will put nurse resources into the specific spotlight [ 1 ]. Indeed, evidence could be used to find solutions for how to solve economic deficits or other problems using leadership skills. This is important as, when nurses are able to show leadership and control in their own work, they are less likely to leave their jobs [ 66 ]. On the other hand, based on our discussions with stakeholders, nurse leaders are not used to using evidence in their own work. Further, evidence-based leadership is not possible if nurse leaders do not have access to a relevant, robust body of evidence, adequate funding, resources, and organizational support, and evidence-informed decision making may only offer short-term solutions [ 55 ]. We still believe that implementing evidence-based strategies into the work of nurse leaders may create opportunities to protect this critical workforce from burnout or leaving the field [ 67 ]. However, the role of the evidence-based approach for nurse leaders in solving these problems is still a key question.
Limitations
This study aimed to use a broad search strategy to ensure a comprehensive review but, nevertheless, limitations exist: we may have missed studies not included in the major international databases. To keep search results manageable, we did not use specific databases to systematically search grey literature although it is a rich source of evidence used in systematic reviews and meta-analysis [ 68 ]. We still included published conference abstract/proceedings, which appeared in our scientific databases. It has been stated that conference abstracts and proceedings with empirical study results make up a great part of studies cited in systematic reviews [ 69 ]. At the same time, a limited space reserved for published conference publications can lead to methodological issues reducing the validity of the review results [ 68 ]. We also found that the great number of studies were carried out in western countries, restricting the generalizability of the results outside of English language countries. The study interventions and outcomes were too different across studies to be meaningfully pooled using statistical methods. Thus, our narrative synthesis could hypothetically be biased. To increase transparency of the data and all decisions made, the data, its categorization and conclusions are based on original studies and presented in separate tables and can be found in Additional files. Regarding a methodological approach [ 34 ], we used a mixed methods systematic review, with the core intention of combining quantitative and qualitative data from primary studies. The aim was to create a breadth and depth of understanding that could confirm to or dispute evidence and ultimately answer the review question posed [ 34 , 70 ]. Although the method is gaining traction due to its usefulness and practicality, guidance in combining quantitative and qualitative data in mixed methods systematic reviews is still limited at the theoretical stage [ 40 ]. As an outcome, it could be argued that other methodologies, for example, an integrative review, could have been used in our review to combine diverse methodologies [ 71 ]. We still believe that the results of this mixed method review may have an added value when compared with previous systematic reviews concerning leadership and an evidence-based approach.
Our mixed methods review fills the gap regarding how nurse leaders themselves use evidence to guide their leadership role and what the measured and perceived impact of evidence-based leadership is in nursing. Although the scarcity of controlled studies on this topic is concerning, the available research data suggest that evidence-based leadership intervention can improve nurse performance, organizational outcomes, and patient outcomes. Leadership problems are also well recognized in healthcare settings. More knowledge and a deeper understanding of the role of nurse leaders, and how they can use evidence in their own managerial leadership decisions, is still needed. Despite the limited number of studies, we assume that this narrative synthesis can provide a good foundation for how to develop evidence-based leadership in the future.
Implications
Based on our review results, several implications can be recommended. First, the future of nursing success depends on knowledgeable, capable, and strong leaders. Therefore, nurse leaders worldwide need to be educated about the best ways to manage challenging situations in healthcare contexts using an evidence-based approach in their decisions. This recommendation was also proposed by nurses and nurse leaders during our discussion meeting with stakeholders.
Second, curriculums in educational organizations and on-the-job training for nurse leaders should be updated to support general understanding how to use evidence in leadership decisions. And third, patients and family members should be more involved in the evidence-based approach. It is therefore important that nurse leaders learn how patients’ and family members’ views as stakeholders are better considered as part of the evidence-based leadership approach.
Future studies should be prioritized as follows: establishment of clear parameters for what constitutes and measures evidence-based leadership; use of theories or models in research to inform mechanisms how to effectively change the practice; conducting robust effectiveness studies using trial designs to evaluate the impact of evidence-based leadership; studying the role of patient and family members in improving the quality of clinical care; and investigating the financial impact of the use of evidence-based leadership approach within respective healthcare systems.
Data availability
The authors obtained all data for this review from published manuscripts.
World Health Organization. State of the world’s nursing 2020: investing in education, jobs and leadership. 2020. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240003279 . Accessed 29 June 2024.
Hersey P, Campbell R. Leadership: a behavioral science approach. The Center for; 2004.
Cline D, Crenshaw JT, Woods S. Nurse leader: a definition for the 21st century. Nurse Lead. 2022;20(4):381–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mnl.2021.12.017 .
Article Google Scholar
Chen SS. Leadership styles and organization structural configurations. J Hum Resource Adult Learn. 2006;2(2):39–46.
Google Scholar
McKibben L. Conflict management: importance and implications. Br J Nurs. 2017;26(2):100–3.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Haghgoshayie E, Hasanpoor E. Evidence-based nursing management: basing Organizational practices on the best available evidence. Creat Nurs. 2021;27(2):94–7. https://doi.org/10.1891/CRNR-D-19-00080 .
Majers JS, Warshawsky N. Evidence-based decision-making for nurse leaders. Nurse Lead. 2020;18(5):471–5.
Tichy NM, Bennis WG. Making judgment calls. Harvard Business Rev. 2007;85(10):94.
Sousa MJ, Pesqueira AM, Lemos C, Sousa M, Rocha Á. Decision-making based on big data analytics for people management in healthcare organizations. J Med Syst. 2019;43(9):1–10.
Guo R, Berkshire SD, Fulton LV, Hermanson PM. %J L in HS. Use of evidence-based management in healthcare administration decision-making. 2017;30(3): 330–42.
Liang Z, Howard P, Rasa J. Evidence-informed managerial decision-making: what evidence counts?(part one). Asia Pac J Health Manage. 2011;6(1):23–9.
Hasanpoor E, Janati A, Arab-Zozani M, Haghgoshayie E. Using the evidence-based medicine and evidence-based management to minimise overuse and maximise quality in healthcare: a hybrid perspective. BMJ evidence-based Med. 2020;25(1):3–5.
Shingler NA, Gonzalez JZ. Ebm: a pathway to evidence-based nursing management. Nurs 2022. 2017;47(2):43–6.
Farokhzadian J, Nayeri ND, Borhani F, Zare MR. Nurse leaders’ attitudes, self-efficacy and training needs for implementing evidence-based practice: is it time for a change toward safe care? Br J Med Med Res. 2015;7(8):662.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
American Nurses Association. ANA leadership competency model. Silver Spring, MD; 2018.
Royal College of Nursing. Leadership skills. 2022. https://www.rcn.org.uk/professional-development/your-career/nurse/leadership-skills . Accessed 29 June 2024.
Kakemam E, Liang Z, Janati A, Arab-Zozani M, Mohaghegh B, Gholizadeh M. Leadership and management competencies for hospital managers: a systematic review and best-fit framework synthesis. J Healthc Leadersh. 2020;12:59.
Liang Z, Howard PF, Leggat S, Bartram T. Development and validation of health service management competencies. J Health Organ Manag. 2018;32(2):157–75.
World Health Organization. Global Strategic Directions for Nursing and Midwifery. 2021. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/344562/9789240033863-eng.pdf . Accessed 29 June 2024.
NHS Leadership Academy. The nine leadership dimensions. 2022. https://www.leadershipacademy.nhs.uk/resources/healthcare-leadership-model/nine-leadership-dimensions/ . Accessed 29 June 2024.
Canadian Nurses Association. Evidence-informed decision-making and nursing practice: Position statement. 2018. https://hl-prod-ca-oc-download.s3-ca-central-1.amazonaws.com/CNA/2f975e7e-4a40-45ca-863c-5ebf0a138d5e/UploadedImages/documents/Evidence_informed_Decision_making_and_Nursing_Practice_position_statement_Dec_2018.pdf . Accessed 29 June 2024.
Hasanpoor E, Hajebrahimi S, Janati A, Abedini Z, Haghgoshayie E. Barriers, facilitators, process and sources of evidence for evidence-based management among health care managers: a qualitative systematic review. Ethiop J Health Sci. 2018;28(5):665–80.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Collins DB, Holton EF III. The effectiveness of managerial leadership development programs: a meta-analysis of studies from 1982 to 2001. Hum Res Dev Q. 2004;15(2):217–48.
Cummings GG, Lee S, Tate K, Penconek T, Micaroni SP, Paananen T, et al. The essentials of nursing leadership: a systematic review of factors and educational interventions influencing nursing leadership. Int J Nurs Stud. 2021;115:103842.
Clavijo-Chamorro MZ, Romero-Zarallo G, Gómez-Luque A, López-Espuela F, Sanz-Martos S, López-Medina IM. Leadership as a facilitator of evidence implementation by nurse managers: a metasynthesis. West J Nurs Res. 2022;44(6):567–81.
Young SK. Evidence-based management: a literature review. J Nurs Adm Manag. 2002;10(3):145–51.
Williams LL. What goes around comes around: evidence-based management. Nurs Adm Q. 2006;30(3):243–51.
Fraser I. Organizational research with impact: working backwards. Worldviews Evidence-Based Nurs. 2004;1:S52–9.
Roshanghalb A, Lettieri E, Aloini D, Cannavacciuolo L, Gitto S, Visintin F. What evidence on evidence-based management in healthcare? Manag Decis. 2018;56(10):2069–84.
Jaana M, Vartak S, Ward MM. Evidence-based health care management: what is the research evidence available for health care managers? Eval Health Prof. 2014;37(3):314–34.
Tate K, Hewko S, McLane P, Baxter P, Perry K, Armijo-Olivo S, et al. Learning to lead: a review and synthesis of literature examining health care managers’ use of knowledge. J Health Serv Res Policy. 2019;24(1):57–70.
Geerts JM, Goodall AH, Agius S, %J SS. Medicine. Evidence-based leadership development for physicians: a systematic literature review. 2020;246: 112709.
Barends E, Rousseau DM, Briner RB. Evidence-based management: The basic principles. Amsterdam; 2014. https://research.vu.nl/ws/portalfiles/portal/42141986/complete+dissertation.pdf#page=203 . Accessed 29 June 2024.
Stern C, Lizarondo L, Carrier J, Godfrey C, Rieger K, Salmond S, et al. Methodological guidance for the conduct of mixed methods systematic reviews. JBI Evid Synthesis. 2020;18(10):2108–18. https://doi.org/10.11124/JBISRIR-D-19-00169 .
Lancet T. 2020: unleashing the full potential of nursing. Lancet (London, England). 2019. p. 1879.
Välimäki MA, Lantta T, Hipp K, Varpula J, Liu G, Tang Y, et al. Measured and perceived impacts of evidence-based leadership in nursing: a mixed-methods systematic review protocol. BMJ Open. 2021;11(10):e055356. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2021-055356 .
The Joanna Briggs Institute. Joanna Briggs Institute reviewers’ manual: 2014 edition. Joanna Briggs Inst. 2014; 88–91.
Pearson A, White H, Bath-Hextall F, Salmond S, Apostolo J, Kirkpatrick P. A mixed-methods approach to systematic reviews. JBI Evid Implement. 2015;13(3):121–31.
Johnson RB, Onwuegbuzie AJ. Mixed methods research: a research paradigm whose time has come. Educational Researcher. 2004;33(7):14–26.
Hong, Pluye P, Bujold M, Wassef M. Convergent and sequential synthesis designs: implications for conducting and reporting systematic reviews of qualitative and quantitative evidence. Syst Reviews. 2017;6(1):61. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-017-0454-2 .
Ramis MA, Chang A, Conway A, Lim D, Munday J, Nissen L. Theory-based strategies for teaching evidence-based practice to undergraduate health students: a systematic review. BMC Med Educ. 2019;19(1):1–13.
Sackett DL, Rosenberg WM, Gray JM, Haynes RB, Richardson WS. Evidence based medicine: what it is and what it isn’t. Bmj. British Medical Journal Publishing Group; 1996. pp. 71–2.
Goodman JS, Gary MS, Wood RE. Bibliographic search training for evidence-based management education: a review of relevant literatures. Acad Manage Learn Educ. 2014;13(3):322–53.
Aromataris E, Munn Z. Chapter 3: Systematic reviews of effectiveness. JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis. 2020; https://synthesismanual.jbi.global .
Munn Z, Barker TH, Moola S, Tufanaru C, Stern C, McArthur A et al. Methodological quality of case series studies: an introduction to the JBI critical appraisal tool. 2020;18(10): 2127–33.
Hong Q, Pluye P, Fàbregues S, Bartlett G, Boardman F, Cargo M, et al. Mixed methods Appraisal Tool (MMAT) Version 2018: user guide. Montreal: McGill University; 2018.
McKenna J, Jeske D. Ethical leadership and decision authority effects on nurses’ engagement, exhaustion, and turnover intention. J Adv Nurs. 2021;77(1):198–206.
Maxwell M, Hibberd C, Aitchison P, Calveley E, Pratt R, Dougall N, et al. The TIDieR (template for intervention description and replication) checklist. The patient Centred Assessment Method for improving nurse-led biopsychosocial assessment of patients with long-term conditions: a feasibility RCT. NIHR Journals Library; 2018.
Braun V, Clarke V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qualitative Res Psychol. 2006;3(2):77–101.
Pollock A, Campbell P, Struthers C, Synnot A, Nunn J, Hill S, et al. Stakeholder involvement in systematic reviews: a scoping review. Syst Reviews. 2018;7:1–26.
Braye S, Preston-Shoot M. Emerging from out of the shadows? Service user and carer involvement in systematic reviews. Evid Policy. 2005;1(2):173–93.
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Syst Reviews. 2021;10(1):1–11.
Porta M. Pilot investigation, study. A dictionary of epidemiology. Oxford University Press Oxford; 2014. p. 215.
Kreis J, Puhan MA, Schünemann HJ, Dickersin K. Consumer involvement in systematic reviews of comparative effectiveness research. Health Expect. 2013;16(4):323–37.
Joseph ML, Nelson-Brantley HV, Caramanica L, Lyman B, Frank B, Hand MW, et al. Building the science to guide nursing administration and leadership decision making. JONA: J Nurs Adm. 2022;52(1):19–26.
Gifford W, Davies BL, Graham ID, Tourangeau A, Woodend AK, Lefebre N. Developing Leadership Capacity for Guideline Use: a pilot cluster Randomized Control Trial: Leadership Pilot Study. Worldviews Evidence-Based Nurs. 2013;10(1):51–65. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1741-6787.2012.00254.x .
Hsieh HY, Henker R, Ren D, Chien WY, Chang JP, Chen L, et al. Improving effectiveness and satisfaction of an electronic charting system in Taiwan. Clin Nurse Specialist. 2016;30(6):E1–6. https://doi.org/10.1097/NUR.0000000000000250 .
McAllen E, Stephens K, Swanson-Biearman B, Kerr K, Whiteman K. Moving Shift Report to the Bedside: an evidence-based Quality Improvement Project. OJIN: Online J Issues Nurs. 2018;23(2). https://doi.org/10.3912/OJIN.Vol23No02PPT22 .
Thomas M, Autencio K, Cesario K. Positive outcomes of an evidence-based pressure injury prevention program. J Wound Ostomy Cont Nurs. 2020;47:S24.
Cullen L, Titler MG. Promoting evidence-based practice: an internship for Staff nurses. Worldviews Evidence-Based Nurs. 2004;1(4):215–23. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-475X.2004.04027.x .
DuBose BM, Mayo AM. Resistance to change: a concept analysis. Nursing forum. Wiley Online Library; 2020. pp. 631–6.
Lalleman PCB, Smid GAC, Lagerwey MD, Shortridge-Baggett LM, Schuurmans MJ. Curbing the urge to care: a bourdieusian analysis of the effect of the caring disposition on nurse middle managers’ clinical leadership in patient safety practices. Int J Nurs Stud. 2016;63:179–88.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Martin E, Warshawsky N. Guiding principles for creating value and meaning for the next generation of nurse leaders. JONA: J Nurs Adm. 2017;47(9):418–20.
Griffiths P, Recio-Saucedo A, Dall’Ora C, Briggs J, Maruotti A, Meredith P, et al. The association between nurse staffing and omissions in nursing care: a systematic review. J Adv Nurs. 2018;74(7):1474–87. https://doi.org/10.1111/jan.13564 .
Lúanaigh PÓ, Hughes F. The nurse executive role in quality and high performing health services. J Nurs Adm Manag. 2016;24(1):132–6.
de Kok E, Weggelaar-Jansen AM, Schoonhoven L, Lalleman P. A scoping review of rebel nurse leadership: descriptions, competences and stimulating/hindering factors. J Clin Nurs. 2021;30(17–18):2563–83.
Warshawsky NE. Building nurse manager well-being by reducing healthcare system demands. JONA: J Nurs Adm. 2022;52(4):189–91.
Paez A. Gray literature: an important resource in systematic reviews. J Evidence-Based Med. 2017;10(3):233–40.
McAuley L, Tugwell P, Moher D. Does the inclusion of grey literature influence estimates of intervention effectiveness reported in meta-analyses? Lancet. 2000;356(9237):1228–31.
Sarah S. Introduction to mixed methods systematic reviews. https://jbi-global-wiki.refined.site/space/MANUAL/4689215/8.1+Introduction+to+mixed+methods+systematic+reviews . Accessed 29 June 2024.
Whittemore R, Knafl K. The integrative review: updated methodology. J Adv Nurs. 2005;52(5):546–53.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We want to thank the funding bodies, the Finnish National Agency of Education, Asia Programme, the Department of Nursing Science at the University of Turku, and Xiangya School of Nursing at the Central South University. We also would like to thank the nurses and nurse leaders for their valuable opinions on the topic.
The work was supported by the Finnish National Agency of Education, Asia Programme (grant number 26/270/2020) and the University of Turku (internal fund 26003424). The funders had no role in the study design and will not have any role during its execution, analysis, interpretation of the data, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Nursing Science, University of Turku, Turku, FI-20014, Finland
Maritta Välimäki, Tella Lantta, Kirsi Hipp & Jaakko Varpula
School of Public Health, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, FI-00014, Finland
Maritta Välimäki
Xiangya Nursing, School of Central South University, Changsha, 410013, China
Shuang Hu, Jiarui Chen, Yao Tang, Wenjun Chen & Xianhong Li
School of Health and Social Services, Häme University of Applied Sciences, Hämeenlinna, Finland
Hunan Cancer Hospital, Changsha, 410008, China
Gaoming Liu
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Study design: MV, XL. Literature search and study selection: MV, KH, TL, WC, XL. Quality assessment: YT, SH, XL. Data extraction: JC, MV, JV, WC, YT, SH, GL. Analysis and interpretation: MV, SH. Manuscript writing: MV. Critical revisions for important intellectual content: MV, XL. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Xianhong Li .

Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
No ethical approval was required for this study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Differences between the original protocol
We modified criteria for the included studies: we included published conference abstracts/proceedings, which form a relatively broad knowledge base in scientific knowledge. We originally planned to conduct a survey with open-ended questions followed by a face-to-face meeting to discuss the preliminary results of the review. However, to avoid extra burden in nurses due to COVID-19, we decided to limit the validation process to the online discussion only.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Supplementary material 2, supplementary material 3, supplementary material 4, supplementary material 5, supplementary material 6, supplementary material 7, supplementary material 8, supplementary material 9, supplementary material 10, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Välimäki, M., Hu, S., Lantta, T. et al. The impact of evidence-based nursing leadership in healthcare settings: a mixed methods systematic review. BMC Nurs 23 , 452 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-024-02096-4
Download citation
Received : 28 April 2023
Accepted : 13 June 2024
Published : 03 July 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-024-02096-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Evidence-based leadership
- Health services administration
- Organizational development
- Quality in healthcare
BMC Nursing
ISSN: 1472-6955
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Evidence-based practice improves patient outcomes and healthcare system return on investment: Findings from a scoping review
Affiliations.
- 1 Helene Fuld Health Trust National Institute for Evidence-Based Practice in Nursing & Healthcare, College of Nursing, The Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio, USA.
- 2 St. John Fisher University, Wegmans School of Nursing, Rochester, New York, USA.
- 3 Sinai Hospital, Baltimore, Maryland, USA.
- 4 Summa Health System, Akron, Ohio, USA.
- 5 The Ohio State University, College of Nursing, Columbus, Ohio, USA.
- 6 Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York, New York, USA.
- 7 Family CareX, Denver, Colorado, USA.
- 8 Affiliate Faculty, VCU Libraries, Health Sciences Library, Virginia Commonwealth University School of Nursing, Richmond, Virginia, USA.
- PMID: 36751881
- DOI: 10.1111/wvn.12621
Background: Evidence-based practice and decision-making have been consistently linked to improved quality of care, patient safety, and many positive clinical outcomes in isolated reports throughout the literature. However, a comprehensive summary and review of the extent and type of evidence-based practices (EBPs) and their associated outcomes across clinical settings are lacking.
Aims: The purpose of this scoping review was to provide a thorough summary of published literature on the implementation of EBPs on patient outcomes in healthcare settings.
Methods: A comprehensive librarian-assisted search was done with three databases, and two reviewers independently performed title/abstract and full-text reviews within a systematic review software system. Extraction was performed by the eight review team members.
Results: Of 8537 articles included in the review, 636 (7.5%) met the inclusion criteria. Most articles (63.3%) were published in the United States, and 90% took place in the acute care setting. There was substantial heterogeneity in project definitions, designs, and outcomes. Various EBPs were implemented, with just over a third including some aspect of infection prevention, and most (91.2%) linked to reimbursement. Only 19% measured return on investment (ROI); 94% showed a positive ROI, and none showed a negative ROI. The two most reported outcomes were length of stay (15%), followed by mortality (12%).
Linking evidence to action: Findings indicate that EBPs improve patient outcomes and ROI for healthcare systems. Coordinated and consistent use of established nomenclature and methods to evaluate EBP and patient outcomes are needed to effectively increase the growth and impact of EBP across care settings. Leaders, clinicians, publishers, and educators all have a professional responsibility related to improving the current state of EBP. Several key actions are needed to mitigate confusion around EBP and to help clinicians understand the differences between quality improvement, implementation science, EBP, and research.
Keywords: evidence-based decision making; evidence-based practice; healthcare; patient outcomes; patient safety; return on investment.
© 2023 The Authors. Worldviews on Evidence-based Nursing published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Sigma Theta Tau International.
Publication types
- Systematic Review
- Delivery of Health Care*
- Evidence-Based Practice* / methods
- Quality Improvement
An official website of the United States government
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Advanced Search
- Journal List

The Impact of Transformational Leadership in the Nursing Work Environment and Patients’ Outcomes: A Systematic Review
Line miray kazin ystaas, monica nikitara, savoula ghobrial, evangelos latzourakis, giannis polychronis, costas s constantinou.
- Author information
- Article notes
- Copyright and License information
Correspondence: [email protected]
Received 2023 Jul 11; Revised 2023 Sep 1; Accepted 2023 Sep 5; Collection date 2023 Sep.
Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ).
Background: With the increasingly demanding healthcare environment, patient safety issues are only becoming more complex. This urges nursing leaders to adapt and master effective leadership; particularly, transformational leadership (TFL) is shown to scientifically be the most successfully recognized leadership style in healthcare, focusing on relationship building while putting followers in power and emphasizing values and vision. Aim: To examine how transformational leadership affects nurses’ job environment and nursing care provided to the patients and patients’ outcomes. Design: A systematic literature review was conducted. From 71 reviewed, 23 studies were included (studies included questionnaire surveys and one interview, extracting barriers and facilitators, and analyzing using qualitative synthesis). Result: TFL indirectly and directly positively affects nurses’ work environment through mediators, including structural empowerment, organizational commitment, and job satisfaction. Nurses perceived that managers’ TFL behavior did not attain excellence in any of the included organizations, highlighting the necessity for additional leadership training to enhance the patient safety culture related to the non-reporting of errors and to mitigate the blame culture within the nursing environment. Conclusion: Bringing more focus to leadership education in nursing can make future nursing leaders more effective, which will cultivate efficient teamwork, a quality nursing work environment, and, ultimately, safe and efficient patient outcomes. This study was not registered.
Keywords: nursing, transformational leadership, work environment, systematic review
1. Introduction
Patient harm caused by errors in healthcare is the leading origin of morbidity and mortality internationally [ 1 ]. Researchers are linking adverse patient safety outcomes to a lack of effective leadership, while relational leadership styles, like transformational leadership, continue to be associated with reduced adverse patient outcomes [ 2 , 3 ]. Nursing is dynamic and requires inspiring and engaging leaders and role models. However, the development of nurse leaders is challenging for the nursing profession.
Currently, nurses face a burnout epidemic rooted mainly in the work environment influenced by excessive workloads and a lack of organizational support and leadership [ 4 ]. Maben et al. (2022) reported that nurses globally face a heightened vulnerability to mental health issues and suicide, surpassing other occupational groups, while the COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated the existing challenges in their work environment, further intensifying the already demanding conditions [ 5 ]. The engagement in emotional labor within the nursing profession exposes practitioners to a notable susceptibility to experiencing burnout, moral distress, and compassion fatigue. Prior to the onset of the pandemic, the international cadre of nurses was already confronting considerable hurdles, encompassing prolonged duty durations, rotation schedules, inadequate staffing, and periodically arduous situations [ 5 , 6 , 7 ]. Throughout the pandemic, nurses encountered a range of stress-inducing factors, including managing heightened public expectations and pressure, adapting to new work responsibilities, facing elevated mortality rates, dealing with the infectious nature of COVID-19, experiencing psychosocial stress, confronting the scarcity of personal protective equipment, handling demanding job requirements, and contending with inadequate psychological support [ 8 ]. At the same time, scholars have found poor working conditions for nurses and inadequate staffing to predict adverse patient outcomes based on the low-quality nursing job atmosphere and the absence of appropriate leadership styles [ 9 , 10 ].
Safety issues in care, such as adverse events, medication errors, falls, and surgery mistakes, have plagued healthcare systems internationally for decades. Several investigations have acknowledged healthcare environments as high-risk with a lack of safety culture, causing long-delayed discharge, disability, or even death [ 2 , 11 ]. Inherently, the nursing profession and current healthcare climate are chaotic, and a positive safety culture has been proven to come from a creditable and visible leader who supports patient safety behaviors [ 12 ]. It is important to recognize that nurses have the highest patient interaction, making nurse leaders central catalysts to positively influencing patient safety culture to reach safer patient outcomes [ 13 , 14 ].
The quality of the nursing work environment is an indicator of nurse satisfaction. A leader who involves staff fosters teamwork, rewards good performance, and encourages motivation can impact the quality of work life [ 15 , 16 ]. The leadership style describes how the leader interacts with others and can be categorized into two main styles: task-oriented and relational [ 17 ]. Historically, leadership theories started with the Great Man Theory during the Industrial Revolution with strong hierarchical leader-centric decision making, focusing on command-and-control, productivity, and seeing the organization as linear, operating like a machine [ 18 ]. This leadership style model in healthcare is no longer sustainable, as proven by a lack of change and persisting patient safety issues. Researchers have found that healthcare innovation requires nonlinear and emergent social processes that result in improved organizational outcomes [ 19 ]. In recent years, the two relational styles, transformational and transactional leadership, have been explored through nursing literature and have become high profile in general healthcare research.
Transformational leadership is composed of four key components. Firstly, “idealized influence” involves the leader behaving as a robust role model toward followers, demonstrating a work ethic and strong values while preaching the organization’s vision, thereby winning the staff’s trust and confidence [ 20 ]. The second type of behavior is referred to as “inspirational motivation”. It includes creating a compelling and inspiring vision for the future and communicating it to followers through emotionally charged speeches, vivid imagery, and captivating symbols. This encourages followers to strive to reach this shared vision, thus creating a deeper level of commitment and higher performance [ 17 ]. The third type of behavior is called “intellectual stimulation”. Intellectual stimulation encourages followers to think outside the box and consider different approaches to everyday issues, enabling them to devise innovative solutions to these problems [ 21 ]. The final category of behaviors is “individualized consideration”, including coaching, helping followers achieve goals, and providing a supportive climate. By carefully listening, leaders can help fulfill those needs [ 22 ]. For instance, some followers might require explicit guidance regarding how to get a job done, while others require the provision of needed resources so they can figure out the solution on their own. Nonetheless, TFL’s four behaviors construct a transformational leader if performed consistently and are found to bring respect and admiration by followers [ 23 ].
1.1. Rational
Healthcare systems are globally facing a crisis, with nurse shortage being a perennial issue. Nurses have the highest patient interaction, making nurse leaders central catalysts in positively influencing patient safety culture to reach safer patient outcomes [ 13 ]. At the same time, negative nursing work environments cultivate dissatisfied nurses who are likely to suffer from emotional exhaustion or burnout because of ineffective leadership [ 14 ]. Amidst these challenges, there is growing recognition of the potential impact of transformational leadership in healthcare settings.
Transformational leadership is characterized by its focus on relationship-building, empowering followers, and emphasizing shared values and vision. This leadership style has been found to positively affect various industries and sectors, including healthcare. However, there remains a gap in knowledge regarding its specific effectiveness in healthcare settings. A comprehensive analysis of the potential benefits of transformational leadership in the healthcare context is warranted. This systematic review aims to address this gap by investigating the effectiveness of transformational leadership and its potential to create better working environments, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes. We have identified a crucial area of inquiry that has not been thoroughly examined in the existing literature—a systematic review that delves into the relationship between transformational leadership and its effects on both the working environment and patient outcomes. We have identified a single literature review from the preceding decade (2002–2012) that focused on the efficacy of transformational leadership in relation to both work environments and patient outcomes [ 24 ]. Considering this, our current investigation is oriented towards delving into scholarly works spanning the subsequent decade (2012–2022), with the intention of comprehensively examining the evolving discourse on this subject matter. By exploring and synthesizing the current body of knowledge on this topic, our study will contribute valuable insights to the field, allowing healthcare organizations to better understand the impact of transformational leadership and make informed decisions regarding their leadership practices.
The significance of this research lies in its potential to shed light on a promising approach to address the pressing challenges faced by healthcare systems—nurse shortage and dissatisfaction—through effective leadership strategies. By providing evidence-based insights, this review seeks to guide healthcare leaders in adopting transformational leadership practices to create a positive work environment for nurses, reducing emotional exhaustion and burnout, and ultimately enhancing patient care and safety.
In conclusion, the dearth of research on the relationship between transformational leadership, work environment, and patient outcomes in healthcare settings highlights the necessity of this review. By examining the effectiveness of transformational leadership and its potential impact on nurses’ well-being and patient outcomes, our study aims to fill this critical gap in knowledge and contribute to the advancement of healthcare leadership practices.
1.2. Objective and Research Question
Having delineated the rationale and imperative for conducting this systematic review, our primary aim was to search, retrieve, and critically evaluate all pertinent studies centered around the concept of transformational leadership, with a particular focus on its efficacy in fostering an improved working environment for nurses and influencing patient outcomes comprehensively and systematically.
Our aim was to synthesize and analyze studies, and therefore, we used the PICo framework for studies to determine a research question. PICo is the simplest of the frameworks to use for qualitative questions; it stands for Population, Interest, and Context and can be used to find a range of primary literature. The Population in our study is nurses; the Interest is transformational leadership, working environments, and patient outcomes; and the Context is hospitals. Based on the PICo framework, we formulated our research question as follows: “What is the impact of transformational leadership on staff nurse work environments and patient outcomes?”
2. Methodology
To effectively accomplish our aim and investigate our research question, we utilized a systematic review approach following the guidelines outlined in the PRISMA 2020 statement [ 25 ]. The PRISMA 2020 checklist is available in Appendix A . In the subsequent subsections, we provide a comprehensive overview of our methodology.
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
Each of the chosen studies incorporated in this systematic review had to fulfill specific inclusion criteria, as outlined in Table 1 provided below.
Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria.
2.2. Information Sources and Search Strategy
We used the following databases to choose the articles: MEDLINE, CINAHL, and SCIENCE DIRECT. The search approach employed the Boolean operator OR between the keywords nurse, working environments, patients’ outcomes, and transformational leadership and comparable MeSH phrases. To refine the search, phrases with diverse meanings were joined using the Boolean operator AND. The search approach used on the EBSCO platform for the aforementioned databases is described in Table 2 We limited the search to journal articles in English with the full text available. However, numerous studies were rejected as they referred to other leadership styles than transformational leadership in addition to other healthcare settings than a nursing work environment.
Search approach.
* The asterisk in Ebsco platform wildcard in search finds words with a common root.
2.3. Selection of Studies Process
Two researchers (the first two authors) conducted independent searches, retrievals, and selections of studies, initially based on three primary criteria: (a) the presence of primary research, (b) the inclusion of transformational leadership as a topic, and (c) relevance to nursing care. Subsequently, additional criteria, such as peer-reviewed articles published in journals or conference proceedings, as well as the publication date, were employed for further refinement. Upon completing the initial selection process, the two researchers engaged in discussions and compiled a list of prospective articles. This list was shared with four other researchers, who collectively determined the final articles to be included in the review, making any necessary additions or removals as deemed appropriate.
2.4. Data Collection Process
The data from the selected studies were independently collected by two researchers. They extracted the components, items, statements, or competencies that had achieved consensus among experts during the final round of each study. Specifically, the following data from each study were extracted: title of the study, authors’ names, publication year, study design, tools, sample characteristics, and summary of main findings and results. Subsequently, the researchers thoroughly reviewed the extracted data multiple times and proceeded to code and identify overarching themes.
2.5. Synthesis Methods
The data were synthesized by content analysis, and the findings were categorized into themes. After carefully examining the results and findings section of a chosen article, an initial set of codes was created. These codes underwent further improvement as more articles were analyzed. Each line of text was assigned a code, and a code tree was utilized to identify emerging themes. From the interpreted meanings, sub-themes were derived and combined. These sub-themes underwent further analysis and were eventually condensed into a single overarching theme. Content analysis can aid in the identification and summarization of submerging key elements within a large body of data during the review process [ 26 ]. The themes of the effectiveness of TFL in the nursing environment were organized according to the content analysis suggested by Zhang and Wildemuth (2009) [ 27 ].
To ensure the validity of the results, a two-level quality assurance process was implemented. The authors of this paper independently followed the review procedure, including coding, categorization, revisiting the studies, and refining the codes and categories. Subsequently, they convened, engaged in discussions, refined the analysis, and finalized the results.
This review was conducted in accordance with the PRISMA statement ( Figure 1 ) [ 25 ], which provides a set of guidelines for conducting reviews and meta-analyses in a comprehensive and systematic manner.
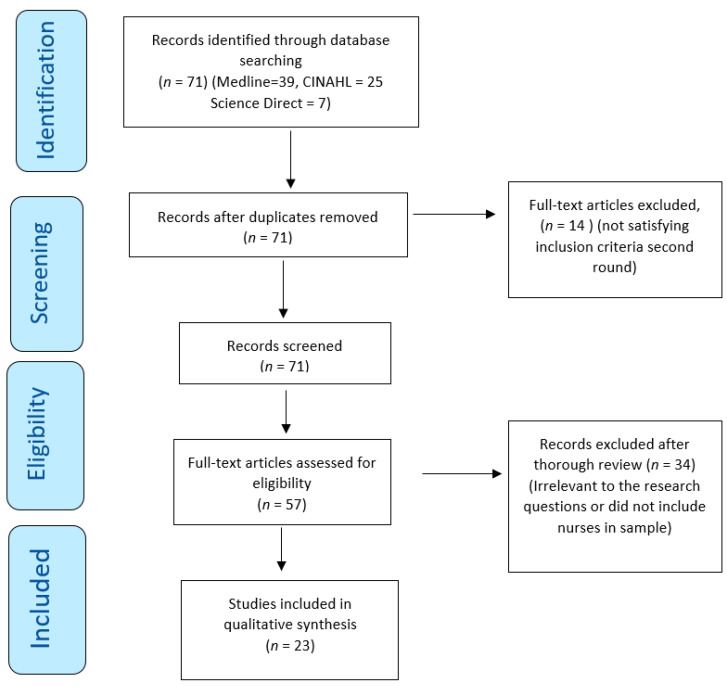
PRISMA flowchart with the search strategy of the systematic review.
3.1. Studies Selection
The initial search process resulted in 71 articles related to transformational leadership. There were no duplications ( Figure 1 ), and therefore, 71 articles were included for advance screening. Fourteen (14) articles did not relate to nurses’ work environment and were omitted. Two researchers thoroughly reviewed the remaining 57 articles independently. From this process, 34 articles were excluded as they did not satisfy the criteria for inclusion. The final number of articles that met the criteria for inclusion was twenty-three (23).
3.2. Studies Characteristics
These 23 articles were conducted in various countries and assessed the effect of transformational leadership in a nursing clinical work environment. Most of the studies included a multifactor leadership questionnaire to evaluate nurses’ perceived effectiveness of transformational leadership (1–10, 13, 14, 16, 18, 19, 22, 23). Further information about the articles, such as author, year, tool, methodology, sample, and main results, is described in Table 3 below.
Articles Description.
3.3. Study Assessment
The quality of the articles included in this review was checked by the Joanna Briggs Institute Qualitative Assessment and Review Instrument Critical Appraisal Checklist. The Joanna Briggs checklist evaluates the methodological quality of a study while determining the possibility of an indication of bias in its conduct, design, and analysis. As can be seen from Table 3 , there were 21 cross-sectional studies (1–11, 13–19, 21–23), 1 descriptive–correlational study (12), and 1 qualitative study (20).
All the included studies largely adhered to the Joanna Briggs criteria, providing comprehensive and detailed descriptions of their respective methodologies and procedures Table 4 , Table 5 and Table 6 . However, it was observed that two of the cross-sectional studies did not explicitly outline any specific strategies to address the stated confounding factors. Nevertheless, as Dekkers et al. (2019) argue, confounding is not dichotomous but rather a continuum where varying degrees of confounding influence can exist [ 28 ]. Furthermore, in accordance with the Joanna Briggs guidelines, the qualitative study failed to disclose the researcher’s cultural or theoretical standpoint, as well as the potential influence of the researcher on the research process. It is worth noting that such omissions are common in qualitative studies, where the focus is on understanding the subjectivity of the participants and allowing their perspectives to emerge naturally.
JBI Critical Appraisal Checklist for Analytical Cross-Sectional Studies.
Risk of Bias Assessed by the Joanna Briggs Institute Critical Appraisal Checklist for Qualitative Study Results.
JBI Critical Appraisal Checklist for Studies Reporting Prevalence Data Results.
3.4. Results of Synthesis
Two major themes emerged, effectively addressing the research questions. Within each theme, several categories were identified, shedding light on the multifaceted nature of the topic under investigation. The themes and their corresponding categories were as follows.
Theme 1: Staff nurses’ work environment:
Job Satisfaction and Organizational Commitment;
Reduce Nurse Retention;
Nurses’ Empowerment and Autonomy;
Nurses’ Compliance with Safety Measures.
Theme 2: Patients’ outcomes:
Patient Safety Culture;
Reporting Adverse Events.
3.4.1. Job Satisfaction and Organizational Commitment
Various studies that investigated the mechanism of TFL detected its strong influence on employee attitudes and behaviors in nursing. Nurses’ work attitudes are reflected in their levels of job satisfaction and organizational commitment [ 29 , 30 ]. It was clear from the literature that TFL frequently positively influenced nurses’ work environment by indirectly increasing job satisfaction [ 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 ]. Employees’ positive perception of jobs and organization is revealed through job satisfaction [ 30 ]. Researchers link TFL and empowerment to the establishment of self-determination and competency, which is proven to impact job satisfaction, suggesting the direct relationship between nurse empowerment and nurse job satisfaction, enhancing the quality of the nurses’ work environment [ 9 , 32 ].
There is also evidence to construct a strong link between organizational commitment and job satisfaction. Interestingly, the statistics showed that nursing staff committed to their organization with a strong sense of loyalty and dependence also had higher levels of job satisfaction [ 29 , 33 ]. Further, higher levels of organizational commitment and job satisfaction were also associated with increased health status in the nurses [ 33 ]. More specifically, TFL was related to more excellent supervisor support, increasing job satisfaction among the nurses, and resulting in more significant organizational commitment [ 29 ]. In a study examining the effectiveness of TFL in the environment of elderly care, TFL was found to effectively strengthen the nursing staff’s sense of belonging to the organization, reducing their burnout. The clan culture established through TFL effectively influenced organizational commitment and job satisfaction, where the atmosphere of a home culture created within their work environment promoted the intrinsic values of nursing staff while improving cohesion between the nurses and the quality of care [ 33 ]. However, TFL was found to have a direct positive effect on organizational commitment [ 33 , 35 ].
3.4.2. Reducing Intention to Leave the Job/Organization
Studies also found that TFL can reduce the nurses’ intent to leave the job, which is closely related to the previous category, as job dissatisfaction can be the primary precursor of nurses’ intent to leave [ 29 ]. The literature generally highlights that the TFL style shapes employees’ perceptions and feelings around their nursing managers and affects their desire and obligation to maintain the intent to stay in their organization [ 36 ]. A recent cross-sectional study examining 645 nurses working during the COVID-19 pandemic found that a supportive workplace culture can construct an adaptive mechanism through which transformational leaders can improve retention [ 37 ]. Additionally, the literature found TFL to decrease emotional exhaustion amongst nurses by encouraging a spiritual climate, indicating that a positive spiritual climate facilitated through TFL can reduce burnout and decrease nursing staff’s intent to leave [ 31 ]. However, there was insufficient evidence proving a direct correlation between TFL and staff nurses’ decision to stay or leave their job [ 33 , 35 ], but it was suggested that TFL has the potential (but not the primary factor) to slow down attrition and retain nurses by improving job satisfaction and organizational commitment, creating a positive work environment and increasing nurses’ probability of staying [ 35 ]. TFL seems to not act directly on job satisfaction or intent to stay but rather create a multifaceted positive work environment leading to a quality nursing environment. Consequently, it was reported that TFL indirectly influenced willingness to stay by positively influencing staff organizational commitment and job satisfaction [ 29 , 33 , 35 ].
3.4.3. Nurses’ Empowerment and Autonomy
Literature highlights that the TFL style within nursing can give staff nurses increased autonomy through empowerment strategies and meaningful participation in decision-making [ 30 , 31 , 36 ]. In turn, TFL-facilitated empowerment has been proven to increase employee commitment within their units by delegating power to nurses, leading to increased authority within their work environment [ 30 , 36 ]. Empowerment through decision-making involvement via removing formal organizational barriers has been found to reduce powerlessness in the nurse work environment, reducing job burnout and increasing job satisfaction [ 30 ]. RN-MD collaboration and teamwork within and across units were thought to be necessary for the nurse’s autonomy [ 38 ]. Further, the literature relates to the concept that a well-functioning patient safety climate requires nurses with autonomy to deal with problems regarding patient safety while proposing specific solutions and getting support and encouragement from organizations to facilitate patient safety-based innovations [ 39 ].
TFL and transactional leadership behaviors were found to affect empowerment amongst the nursing staff positively. However, TFL behaviors allowed nursing managers to reach even higher levels of success without congruence and reward, embedding empowerment into the clinical environment [ 40 ]. Some studies also identified the empowerment subscale, autonomy, as the statistically significant predictor of commitment, indicating that managers can engage nurses in appropriate decision making about patient care and safety in their work environment [ 30 , 36 ]. Management that does not accept decision-making participation dissembles empowerment, which frustrates and makes staff dependent on an authoritarian structure [ 36 ].
3.4.4. Nurses’ Compliance with Safety Measures
Lievens and Vlerick (2014) found a strong association between TFL and nurse safety compliance [ 41 ]. The more transformational the leader was perceived, the more the nursing staff participated and complied with patient safety practices. Further, staff nurses’ structural empowerment also experienced a significant correlation with the degree to which they perceived nursing managers’ (NMs) TFL behaviors [ 36 , 40 ]. Research also suggested that when nurses perceived their TFL to facilitate an innovative work climate, they automatically contributed to developing innovation behaviors [ 39 ]. Previously mentioned research suggested that nurses need to feel a part of their work environment. However, countries where staff are hesitant to challenge authority create a reluctance to change, and compliance can breed a lack of stimulation [ 31 ]. It was reported that nurse managers should be trained to challenge nurses to resolve problems and specialize their competence to foster innovation and grow talents and creativity [ 36 ].
Lievens and Vlerick (2014), in their cross-sectional study which included 145 nurses, also found intellectual stimulation to strongly impact knowledge-related characteristics, suggesting an indirect link between safety performance and TFL through skills and ability demands, where the more knowledge-related job characteristics were perceived, the more nurses complied with safety rules [ 41 ]. Skill utilization or intellectual stimulation was further found to be the strongest single predictor of work engagement, compared to TFL, where nurses appreciated opportunities for personal development, learning new things, and achieving something meaningful, encouraging work engagement [ 2 , 42 ].
Patients’ outcomes:
The literature shows a positive relationship between TFL and the improvement of patient safety climate and culture, emphasizing that nursing managers are key to developing a safety climate and maintaining a culture of patient safety, preventing adverse events.
3.4.5. Increase Patient Safety Culture
There was a significant prevalence of findings reporting TFL to facilitate patient safety either directly [ 2 , 9 , 38 , 42 ] or indirectly [ 32 , 39 , 41 ]. Seljemo et al. (2020), in their cross-sectional study, questioned 156 nurses; Ree and Wiig (2019), also in a cross-sectional design study, questioned 139 nurses and found TFL to be the strongest predictor of patient safety culture and overall perception of patient safety compared to job demands and resources [ 2 , 42 ]. This was suggested to result from TFL having a positive direct effect on the psychosocial work environment. Further evidence also links TFL directly to quality patient outcomes, reducing the possibility of adverse patient outcomes and increasing the quality of care [ 9 ].
Patient safety culture includes themes such as teamwork within units, managers’ support, organizational learning, overall perceptions of safety, feedback and communication openness about the error, frequency of events reported, staffing, handoffs and transitions, and non-punitive response to errors. “Teamwork within units” generally had a common positive perception amongst the nurses, indicating collaboration within their units as effective within TFL [ 38 , 43 , 44 ]. Anselmann and Mulder (2020) asked 183 geriatric nurses in their cross-sectional study, and they support the above, finding that TFL has a positive impact on team performance when a safe climate is fostered [ 45 ]. Even though nurses found cohesion within their units, literature revealed a common theme of insufficient “teamwork between units”, indicating that each unit had an independent culture [ 38 , 43 , 44 ]. Further, a generally weak perception of the effectiveness of RN-MD collaboration was also observed [ 38 , 43 ].
Researchers stressed the necessity of having efficient teamwork between units and on a multi-professional level to create an effective patient safety culture [ 9 ]. Another reoccurring subdimension, “feedback and rewarding”, was also identified as a weak component of TFL in relation to patient safety culture, illustrating a lack of adaptation and implementation of TLF behavior [ 9 , 43 , 46 ]. The TFL nursing manager generally seemed to conduct insufficient work around feedback and rewards, resulting in staff nurses not being encouraged and ensuring that medical errors were prevented and learned from [ 43 , 46 ].
3.4.6. Reporting Adverse Events
Adverse events can result in patient disability or death, prolong the time necessary to provide care, and increase healthcare costs and patient dissatisfaction [ 47 ]. However, a part of the literature showed that when TFL and transactional leadership were compared, reporting errors without blame and discussing errors openly were the two initiatives that transactional leadership implemented better than TFL [ 40 , 48 ]. A significant finding in the literature was the reoccurring theme of weak patient safety culture in relation to “non-punctual reporting of adverse events” in hospitals with TFL, where staff nurses rarely reported occurring medical errors to their NMs [ 34 , 44 , 46 , 48 , 49 ]. In a Finnish study, one in four nurses showed to not have reported one or more medication errors using their units’ adverse event registration system [ 46 ]. Tekingündüz et al. (2021), in a cross-sectional study with 150 participating nurses, also found a significant weakness in their organization’s patient safety culture, where 52.7% of the nurses did not report any adverse events in the last 12 months, 31.3% reported 1–2 adverse events while 10% reported 3–5 adverse events [ 49 ]. Further, in a qualitative study, the eleven nurse manager participants expressed the importance of nursing staff reporting the occurrence of adverse events to detect why each event happened and identify patient safety risks and solutions [ 50 ]. There was evidence to suggest that nurses reported that the occurrence of errors only sometimes led to a positive change, whereas at other times, it did not lead to any change, and errors were repeated [ 38 ]. The literature explained blame culture and fear in the nurse’s work environment as a factor distancing them from punctuative reporting of medical errors [ 46 , 49 , 50 ]. It was suggested by researchers that nursing staff were not encouraged to report and discuss adverse events openly and blame-free [ 48 , 49 , 50 ]. This involves handling adverse reports by nursing managers without making nursing staff feel guilty.
Managers reported that a culture where it is recognized that everyone makes mistakes is imperial, while it was observed that nurses tended to report other colleagues’ mistakes compared to their own [ 50 ]. Further, nursing managers noticed that nursing staff may blame themselves for a patient safety incident where they feel ashamed and worry about their colleague’s perception of them [ 49 ]. These perceptions were confirmed by nursing staff in another study, expressing their tendency to avoid reporting due to fear of punishment, humiliation, damage to reputation, disciplinary action by a licensing board, malpractice lawsuits, and limited follow-up after reporting loss of job [ 48 ]. Tekingündüz et al. (2021) also found the defect in reporting medical errors to be rooted in nurse’s fear of punishment and lack of confidentiality [ 49 ]. Generally, fear was perceived as a major reason for not reporting adverse events, and nursing managers saw this as a barrier to the effectiveness of their leadership and the attempt to develop their operational models to improve patient safety [ 46 , 49 , 50 ]. However, visionary leadership styles such as TFL correlate positively with both incident reporting and patient safety outcomes. Additionally, TFL is linked to improved patient safety, including reduced mortality rates, fewer medication errors, lower incidences of pneumonia and urinary tract infections, and fewer patient falls, attributed to the leaders’ approach of using errors as chances to enhance processes and promoting the reporting of near misses and adverse events [ 17 , 51 ].
Interestingly, a part of the literature showed that when TFL and transactional leadership were compared, reporting errors without blame and discussing errors openly were the two initiatives that transactional leadership implemented better than TFL [ 40 , 48 ]. These findings confirm the weakness around reporting adverse events and blame culture within TFL units.
4. Discussion
This review has collectively reviewed literature that has examined the effectiveness of transformational leadership (TFL) in a nursing work environment and patients’ outcomes. TFL has a complex, interconnected effect on nurses’ intrinsic environment and patient outcomes.
Nurses’ Work Environment:
The literature revealed substantial evidence that TFL can significantly enhance nurses’ psychosocial work environment by indirectly increasing job satisfaction. Three significant mediators between TFL and job satisfaction were nurse empowerment, organizational commitment, and spiritual climate, which altogether were thought to prevent retention in nursing [ 29 , 30 , 31 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 37 ]. Simultaneously, TFL was not the primary factor in job satisfaction but instead a facilitator and constructor of structural empowerment, organizational commitment, and spiritual climate. It is, therefore, evident that the literature revealed a positive domino effect that transformational leaders in nursing can generate. Generally, the literature revealed a strongly positive relationship between TFL and workplace culture in nursing [ 33 , 37 ]. Specific TFL attributes created an inclusive and supportive work environment, either directly or indirectly enhancing the nurses’ work environment and decreasing the risk of nurse burnout [ 37 , 52 ]. Nurses continuously reported managers’ support as a particularly important resource in their work environment, where establishing a high-quality relationship with their leaders was seen as imperial for patient safety culture [ 38 , 42 ].
The correlation observed between supportive leadership and favorable patient safety outcomes underscores the significance of Transformational Leaders (TFLs) possessing a comprehensive grasp of patient safety protocols, as well as recognizing the pivotal role played by bedside nurses in advancing improved safety outcomes. [ 17 ]. More specifically, managers’ support was also found to reinforce innovative behavior [ 39 ], increase job satisfaction [ 35 , 37 ], and even be the primary factor in a positive work environment, compared to TFL [ 29 ]. Conversely, the literature also described managers’ support as a core transformational behavior, where the more transformational the leader was perceived, the more the staff nurses experienced individual support in their clinical environment [ 29 , 42 , 46 ]. As concluded by the literature, TFL is not the primary factor but rather a mediator to job satisfaction, which was determined as an essential nursing outcome, shadowing quality work environment and may be an effective retention strategy in nursing. Previous studies confirm that safety outcomes are improved when workplace empowerment takes place in a positive nurse–leader relationship based on trust and respect, where they, together, work toward a patient safety culture [ 53 ].
Therefore, incorporating transformational leadership in nursing has numerous implications, with a direct and positive impact on job satisfaction. By nurturing a sense of purpose, providing support and empowerment, and promoting individual growth, transformational leaders create a fulfilling work environment that motivates nurses to excel. As nurses experience greater job satisfaction, patient care quality also improves, resulting in cooperative success for healthcare organizations, nursing staff, and the patients they serve.
Patients’ Outcomes:
The connection between supportive leadership and positive patient safety outcomes points to the importance of the TFL’s understanding of patient safety processes and the role of bedside nurses in promoting better safety outcomes [ 38 ]. However, several researchers reported not having a visible leader [ 43 ], which is documented as essential for patient safety changes to occur [ 53 ].
Researchers are linking negative patient safety outcomes to a lack of effective leadership, while relational leadership styles like transformational leadership continue to be associated with reduced adverse patient outcomes [ 17 ]. However, TFL nursing managers were repeatedly reported by the staff nurses only to communicate errors and problems after the adverse event, waiting for the event before resolving problems and taking proactive action [ 36 , 50 ]. Literature highlights that organizations that have successfully created a non-blame culture have better patient safety outcomes because the staff are encouraged to report errors, unsafe practices, and adverse events, perceiving safety around seeking help and assistance without threat [ 54 ]. Therefore, avoiding a blame culture and developing a reporting system serves as a proactive approach to identifying and mitigating risks, ultimately preventing errors and recurring mistakes, which, when left unaddressed, can result in significant social and economic burdens due to fatalities and preventable incidents [ 51 ] Additionally, developing a safety culture through managers’ interdisciplinary walkabout safety rounds has been associated with safety outcomes [ 17 ].
Transformational leadership in nursing has far-reaching implications for patient outcomes and care quality. By fostering a collaborative and patient-centered approach, empowering nursing staff, encouraging continuous learning, and promoting a culture of excellence, transformational leaders enhance the overall care experience for patients. Ultimately, the positive impact of transformational leadership on patient outcomes establishes it as a key factor in ensuring the delivery of high-quality healthcare services in nursing settings.
This literature review enriches nursing practice and research in a time where nursing leaders are sought to have an important and prominent role in healthcare policy development and improvement. Increased demand and complexity of patient care require effective and competent leadership skills and an understanding of TFL’s function in the current healthcare environment. Even though literature has constructed the idea of the nexus between patient safety and leadership, patient safety outcomes are unlikely to improve without facilitating and fostering the professional growth of future leaders. Additionally, factors influencing organizational job satisfaction and organizational commitment are significantly under the influence of TF nurse leaders. Therefore, healthcare organizations and the educational sector should invest in leadership training and curriculum to implement it further into nursing to support and ensure safe, quality work environments for both nurses and patients.
5. Limitations of the Study
This literature review predominantly incorporated quantitative research methodologies, which, in certain instances, can present challenges in contextualizing a phenomenon comprehensively, as the data may not always possess the robustness required to elucidate intricate issues. Additionally, it should be noted that the review’s scope was confined to studies published exclusively in the English language, with no inclusion of relevant content from the grey literature beyond the stipulated publication sources, and unpublished dissertations were also omitted from consideration. Consequently, it is essential to acknowledge that this review may not provide a fully representative overview of all pertinent scholarship within the field.
6. Conclusions
Despite the global recognition and attempted implementation of TFL in healthcare, the statistics still show that TFL is yet to be mastered within nursing. The strong relationship between TFL, structural empowerment, job satisfaction, and organizational commitment signify that an improved quality work environment may be the most essential element to enhance job effectiveness and patient safety in nursing. TFL is a vital facilitator that could help healthcare to improve job satisfaction and reduce adverse events. Evidence suggests that nursing managers who possess effective TFL attributes are likely to influence their nursing staff’s satisfaction and mitigate the risk of burnout by establishing a supportive and inclusive work environment directly or indirectly. Focusing on the adoption of a blame-free culture through effective leadership is likely to break down barriers to safety culture, which has resulted in poor patient care worldwide. Patient safety outcomes rely on a well-established patient safety culture, which is most influenced by the bedside nurse, either directly or indirectly. With effective leadership engagement and education, emerging nursing leaders can be supported while the nursing team can be empowered to make the necessary changes to reach levels of excellence within their units. It is important to comprehend that leaders are not just in executive and senior positions but include any part of the healthcare team that is influential to patient care. Effective TFL engagement has the potential to enhance patient safety, where it is conveyed that all healthcare workers, from executive to bedside nurses, participate in a positive safety culture.
PRISMA 2020 Checklist.
From: Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021;372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71. For more information, visit: http://www.prisma-statement.org/ , access on 26 March 2023.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, search, coding, and drafting, L.M.K.Y. and M.N.; search and quality assurance, coding, and feedback, S.G., E.L., G.P. and C.S.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Data availability statement.
The articles’ data supporting this systematic review are from previously reported studies and datasets, which have been cited. The processed data are available in Table 2 and in the reference list. Further information can be requested from the corresponding author.
Public Involvement Statement
No public involvement in any aspect of this research.
Guidelines and Standards Statement
This manuscript was drafted against the PRISMA 2020 Statement. A complete checklist is found in Appendix A of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Funding Statement
This research received no external funding.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
- 1. Panagioti M., Khan K., Keers R.N., Abuzour A.S., Phipps D., Kontopantelis E., Bower P., Campbell S., Haneef R., Avery A.J., et al. Prevalence, severity, and nature of preventable patient harm across medical care settings: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2019;366:l4185. doi: 10.1136/bmj.l4185. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 2. Ree E., Wiig S. Employees’ perceptions of patient safety culture in Norwegian nursing homes and home care services. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2019;19:607. doi: 10.1186/s12913-019-4456-8. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 3. Cummings G.G., MacGregor T., Davey M., Lee H., Wong C.A., Lo E., Muise M., Stafford E. Leadership styles and outcome patterns for the nursing workforce and work environment: A systematic review. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2010;47:363–385. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2009.08.006. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 4. Alves P.C., Oliveira A.D.F., Paro H. Quality of life and burnout among faculty members: How much does the field of knowledge matter? PLoS ONE. 2019;14:e0214217. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0214217. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 5. Maben J., Conolly A., Abrams R., Rowland E., Harris R., Kelly D., Kent B., Couper K. “You can’t walk through water without getting wet” UK nurses’ distress and psychological health needs during the COVID-19 pandemic: A longitudinal in-terview study. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2022;131:104242. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2022.104242. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 6. Kim M.-N., Yoo Y.-S., Cho O.-H., Hwang K.-H. Emotional Labor and Burnout of Public Health Nurses during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Mediating Effects of Perceived Health Status and Perceived Organizational Support. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2022;19:549. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19010549. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 7. Fahmy A.M., Saber E.H., Gabra S.F. Relation between Compassion Fatigue, Pandemic Emotional Impact, and Time Management among Nurses at Isolation Hospitals during COVID-19. Minia Sci. Nurs. J. 2022;012:57–68. doi: 10.21608/msnj.2022.163882.1037. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 8. Shivairová O., Bártlová S., Hellerová V., Chloubová I. Nurseʼs mental health during COVID-19 pandemic. Cent. Eur. J. Nurs. Midwifery. 2023;14:795–804. doi: 10.15452/cejnm.2022.13.0009. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 9. Asif M., Jameel A., Hussain A., Hwang J., Sahito N. Linking Transformational Leadership with Nurse-Assessed Adverse Patient Outcomes and the Quality of Care: Assessing the Role of Job Satisfaction and Structural Empowerment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2019;16:2381. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16132381. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 10. Labrague L.J. Influence of nurse managers’ toxic leadership behaviours on nurse-reported adverse events and quality of care. J. Nurs. Manag. 2020;29:855–863. doi: 10.1111/jonm.13228. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 11. Farokhzadian J., Nayeri N.D., Borhani F. The long way ahead to achieve an effective patient safety culture: Challenges perceived by nurses. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2018;18:654. doi: 10.1186/s12913-018-3467-1. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 12. Pronovost P.J., Cleeman J.I., Wright D., Srinivasan A. Fifteen years after To Err is Human: A success story to learn from: Table 1. BMJ Qual. Saf. 2015;25:396–399. doi: 10.1136/bmjqs-2015-004720. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 13. Hendricks J., Cope V., Baum G. Postgraduate nurses’ insights into the nursing leadership role. Do they intuitively link the role to patient safety? J. Nurs. Educ. Pract. 2015;5:72–77. doi: 10.5430/jnep.v5n9p72. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 14. Murray M., Sundin D., Cope V. The nexus of nursing leadership and a culture of safer patient care. J. Clin. Nurs. 2017;27:1287–1293. doi: 10.1111/jocn.13980. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 15. Suratno K. The relationship between transformational leadership and quality of nursing work life in hospital. Int. J. Caring Sci. 2018;11:1416–1422. [ Google Scholar ]
- 16. Gottlieb L.N., Gottlieb B., Bitzas V. Creating Empowering Conditions for Nurses with Workplace Autonomy and Agency: How Healthcare Leaders Could Be Guided by Strengths-Based Nursing and Healthcare Leadership (SBNH-L) J. Healthc. Leadersh. 2021;13:169–181. doi: 10.2147/JHL.S221141. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 17. Wong C.A., Cummings G.G., Ducharme L. The relationship between nursing leadership and patient outcomes: A systematic review update. J. Nurs. Manag. 2013;21:709–724. doi: 10.1111/jonm.12116. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 18. Weberg D.R., Davidson S. Leadership for Evidence-Based Innovation in Nursing and Health Professions. 2nd ed. Jones & Bartlett Learning; Burlington, MA, USA: 2022. [ Google Scholar ]
- 19. Schein H., Schein P.A. Organizational Culture and Leadership. 5th ed. Wiley; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2016. [ Google Scholar ]
- 20. Bass B.M., Riggio R.E. Transformational Leadership. Psychology Press; London, UK: 2006. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 21. Bass B.M. Theory of transformational leadership redux. Leadersh. Q. 1996;6:463–478. doi: 10.1016/1048-9843(95)90021-7. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 22. Bass B.M., Avolio B.J., Jung D.I., Berson Y. Predicting unit performance by assessing transformational and transactional leadership. J. Appl. Psychol. 2003;88:207–218. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.88.2.207. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 23. Lu Q., Liu Y., Huang X. Follower Dependence, Independence, or Interdependence: A Multi-Foci Framework to Unpack the Mystery of Transformational Leadership Effects. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2020;17:4534. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17124534. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 24. Hutchinson M., Jackson D. Transformational leadership in nursing: Towards a more critical interpretation. Nurs. Inq. 2012;20:11–22. doi: 10.1111/nin.12006. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 25. Page M.J., McKenzie J.E., Bossuyt P.M., Boutron I., Hoffmann T.C., Mulrow C.D., Shamseer L., Tetzlaff J.M., Akl E.A., Brennan S.E., et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021;372:71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 26. Mikkonen K., Kääriäinen M. Content Analysis in Systematic Reviews. In: Kyngäs H., Mikkonen K., Kääriäinen M., editors. The Application of Content Analysis in Nursing Science Research. Springer; Cham, Switzerland: 2020. [ Google Scholar ]
- 27. Zhang Y., Wildemuth B.M. Qualitative analysis of content. In: Wildemuth B., editor. Applications of Social Research Methods to Questions in Information and Library Science. Libraries Unlimited; Westport, CT, USA: 2009. pp. 308–319. [ Google Scholar ]
- 28. Dekkers O.M., Vandenbroucke J.P., Cevallos M., Renehan A.G., Altman D.G., Egger M. COSMOS-E: Guidance on conducting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of observational studies of etiology. PLoS Med. 2019;16:e1002742. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002742. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 29. Lin P.-Y., MacLennan S., Hunt N., Cox T. The influences of nursing transformational leadership style on the quality of nurses’ working lives in Taiwan: A cross-sectional quantitative study. BMC Nurs. 2015;14:33. doi: 10.1186/s12912-015-0082-x. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 30. Choi S.L., Goh C.F., Adam M.B.H., Tan O.K. Transformational leadership, empowerment, and job satisfaction: The mediating role of employee empowerment. Hum. Resour. Health. 2016;14:73. doi: 10.1186/s12960-016-0171-2. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 31. Wu X., Hayter M., Lee A.J., Yuan Y., Li S., Bi Y., Zhang L., Cao C., Gong W., Zhang Y. Positive spiritual climate supports transformational leadership as means to reduce nursing burnout and intent to leave. J. Nurs. Manag. 2020;28:804–813. doi: 10.1111/jonm.12994. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 32. Boamah S.A., Laschinger H.K.S., Wong C., Clarke S. Effect of transformational leadership on job satisfaction and patient safety outcomes. Nurs. Outlook. 2018;66:180–189. doi: 10.1016/j.outlook.2017.10.004. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 33. Xie Y., Gu D., Liang C., Zhao S., Ma Y. How transformational leadership and clan culture influence nursing staff’s willingness to stay. J. Nurs. Manag. 2020;28:1515–1524. doi: 10.1111/jonm.13092. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 34. Wagner A., on behalf of the WorkSafeMed Consortium. Rieger M.A., Manser T., Sturm H., Hardt J., Martus P., Lessing C., Hammer A. Healthcare professionals’ perspectives on working conditions, leadership, and safety climate: A cross-sectional study. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2019;19:53. doi: 10.1186/s12913-018-3862-7. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 35. Brewer C.S., Kovner C.T., Djukic M., Fatehi F., Greene W., Chacko T.P., Yang Y. Impact of transformational leadership on nurse work outcomes. J. Adv. Nurs. 2016;72:2879–2893. doi: 10.1111/jan.13055. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 36. Asiri S.A., Rohrer W.W., Al-Surimi K., Da’ar O.O., Ahmed A. The association of leadership styles and empowerment with nurses’ organizational commitment in an acute health care setting: A cross-sectional study. BMC Nurs. 2016;15:38. doi: 10.1186/s12912-016-0161-7. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 37. Boamah S.A. The impact of transformational leadership on nurse faculty satisfaction and burnout during the COVID-19 pandemic: A moderated mediated analysis. J. Adv. Nurs. 2022;78:2815–2826. doi: 10.1111/jan.15198. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 38. El-Demerdash A.M.S., Elhosany W.A., Hefny M.A.M. Professional Forces of Magnetism and Patient Safety Culture at Suez Canal University Hospitals. Int. J. Nurs. Didact. 2018;8:10–18. doi: 10.15520/ijnd.2018.vol8.iss01.269.10-18. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 39. Weng R.-H., Huang C.-Y., Chen L.-M., Chang L.-Y. Exploring the impact of transformational leadership on nurse innovation behaviour: A cross-sectional study. J. Nurs. Manag. 2013;23:427–439. doi: 10.1111/jonm.12149. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 40. Khan B.P., Griffin M.T.Q., Fitzpatrick J.J. Staff Nurses’ Perceptions of Their Nurse Managers’ Transformational Leadership Behaviors and Their Own Structural Empowerment. JONA J. Nurs. Adm. 2018;48:609–614. doi: 10.1097/NNA.0000000000000690. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 41. Lievens I., Vlerick P. Transformational leadership and safety performance among nurses: The mediating role of knowledge-related job characteristics. J. Adv. Nurs. 2013;70:651–661. doi: 10.1111/jan.12229. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 42. Seljemo C., Viksveen P., Ree E. The role of transformational leadership, job demands and job resources for patient safety culture in Norwegian nursing homes: A cross-sectional study. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2020;20:799. doi: 10.1186/s12913-020-05671-y. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 43. Kvist T., Mäntynen R., Turunen H., Partanen P., Miettinen M., Wolf G.A., Vehviläinen-Julkunen K. How magnetic are Finnish hospitals measured by transformational leadership and empirical quality outcomes? J. Nurs. Manag. 2012;21:152–164. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2834.2012.01456.x. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 44. Yilmaz A., Duygulu S. The Relationship Between Charge Nurses and Clinical Nurses’ Perceptions of Patient Safety Culture and Leadership Practices. Dokuz Eylül Üniversitesi Hemşirelik Fakültesi Elektron. Derg. 2021;14:29–37. doi: 10.46483/deuhfed.743446. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 45. Anselmann V., Mulder R.H. Transformational leadership, knowledge sharing and reflection, and work teams’ performance: A structural equation modelling analysis. J. Nurs. Manag. 2020;28:1627–1634. doi: 10.1111/jonm.13118. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 46. Lappalainen M., Härkänen M., Kvist T. The relationship between nurse manager’s transformational leadership style and medication safety. Scand. J. Caring Sci. 2019;34:357–369. doi: 10.1111/scs.12737. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 47. Mansouri S.F., Mohammadi T.K., Adib M., Lili E.K., Soodmand M. Barriers to nurses reporting errors and adverse events. Br. J. Nurs. 2019;28:690–695. doi: 10.12968/bjon.2019.28.11.690. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 48. Alfadhalah T., Elamir H. Patient safety and leadership style in the government general hospitals in Kuwait: A multi-method study. Leadersh. Health Serv. 2021;35:190–209. doi: 10.1108/LHS-07-2021-0062. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 49. Tekingündüz S., Yıldız E., İnci R. Relationships Between Nurses’ Perceptions of Patient Safety Culture and Job Stress, Trust, Identification, and Leadership. Leadership. 2021;8:344–354. doi: 10.54304/SHYD.2021.59389. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 50. Liukka M., Hupli M., Turunen H. How transformational leadership appears in action with adverse events? A study for Finnish nurse manager. J. Nurs. Manag. 2017;26:639–646. doi: 10.1111/jonm.12592. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 51. Merrill K.C. Leadership Style and Patient Safety. JONA J. Nurs. Adm. 2015;45:319–324. doi: 10.1097/NNA.0000000000000207. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 52. Burns K.E.A., Pattani R., Lorens E., Straus S.E., Hawker G.A. The impact of organizational culture on professional fulfillment and burnout in an academic department of medicine. PLoS ONE. 2021;16:e0252778. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252778. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 53. Murray M., Cope V. Leadership: Patient safety depends on it! Collegian. 2021;28:604–609. doi: 10.1016/j.colegn.2021.07.004. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 54. O’connor S., Carlson E. Safety Culture and Senior Leadership Behavior. JONA J. Nurs. Adm. 2016;46:215–220. doi: 10.1097/NNA.0000000000000330. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
- View on publisher site
- PDF (477.5 KB)
- Collections
Similar articles
Cited by other articles, links to ncbi databases.
- Download .nbib .nbib
- Format: AMA APA MLA NLM
Add to Collections

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The American Journal of Nursing (AJN) is the oldest and largest circulating nursing journal in the world. The Journal's mission is to promote excellence in professional nursing, with a global perspective, by providing cutting edge, evidence-based information that embraces a holistic perspective on health and nursing. Clinical articles focus on ...
Exploring all aspects of nursing research, training, education, and practice, BMC Nursing is a well-established open access peer-reviewed journal. Rapid ...
Health Source, Nursing/Academic Edition provides nearly 550 scholarly full text journals, including nearly 450 peer-reviewed journals focusing on many medical disciplines. Also featured are abstracts and indexing for nearly 850 journals. Coverage of nursing and allied health is particularly strong.
Nursing students' preparation and nurse clinicians' continuing education are increasingly important not only due to the disparities in health outcomes described above, but also due to the increasing diversity of the U.S. population as a whole. ... [PMC free article] [Google Scholar] Fleckman JM, Corsco MD, Ramirez S, Begaleiva M, Johnson CG ...
The shortage of nurses has resulted in an increasing workload for existing nurses, significantly affecting their work life and performance, which can have a direct impact on the quality of care delivered. 4 Nursing performance is influenced by cognitive, physical, and organizational factors. 5 Various factors such as high workloads, lack of technological support, 6 skills and competencies (eg ...
The central component in impactful healthcare decisions is evidence. Understanding how nurse leaders use evidence in their own managerial decision making is still limited. This mixed methods systematic review aimed to examine how evidence is used to solve leadership problems and to describe the measured and perceived effects of evidence-based leadership on nurse leaders and their performance ...
1 Helene Fuld Health Trust National Institute for Evidence-Based Practice in Nursing & Healthcare, College of Nursing, The Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio, USA. ... Results: Of 8537 articles included in the review, 636 (7.5%) met the inclusion criteria. Most articles (63.3%) were published in the United States, and 90% took place in the ...
Literature describing nursing care (concepts and theories on nursing care) Abstracts, discussion articles, non-research articles, systematic reviews, anecdotal reports or editorials, conference proceedings, dissertations and concept analysis: Published/dealing with Europe (incl. UK, Irland), Australia, New Zealand and North America (USA, Canada)
Abstract. Background: With the increasingly demanding healthcare environment, patient safety issues are only becoming more complex. This urges nursing leaders to adapt and master effective leadership; particularly, transformational leadership (TFL) is shown to scientifically be the most successfully recognized leadership style in healthcare, focusing on relationship building while putting ...
This study focuses on Code of Ethics for Nurses with Interpretive Statements published by the American Nurses Association (hereafter the Code). 2 American Nurses Association (ANA) is a national nursing organization representing the interests of more than five million registered nurses. ANA advances the profession fostering high standards of nursing practice, promoting a safe and ethical work ...