Engineering Physics Viva
…..And Then There Is Physics

Bi-quartz Polarimeter
Q.What is Polarimeter ?
A.It is a device used to measure the angle of rotation of plane of polarisation rotated by an optically active substance.
Q.What is specific rotation ?
A.Specific rotation of an optically active substance at a given temperature is the rotation in degrees of the plane of polarisation of incident polarized beam produced by one decimeter length of substance of unit concentration.
Q.What are optically active substances?
A.Optically active substances rotate the plane of polarisation or plane of vibration of plane polarised light when it passes through it.
Q.What are different optically active substances?
A. Right handed or dextro rotatory & left handed or leavo rotatory
Q.Define plane of polarisation
A.It is the plane passing through the direction of propagation of light.
Q.Define plane polarised light.
A.Light is said to be plane polarised if it has vibrations in a single direction perpendicular to direction of propagation.
Q.Define plane of vibration.
A.It is the plane containing the direction of vibration and direction of propagation.
Q.How does specific rotation depend on temperature?
A.In some substances it decreases with rise in temperature like turpentine while in quartz it increases.
Q.What is the unit of specific rotation?
A.degree/decimeter/gm/cc
Q.name one practical use of polarimeter.
A.It is used to measure percentage of sugar in a solution.
Q.What is the function of analyzer and polariser ?
A. Polariser changer ordinary light to plane polarised light and analyzer is used to analyse light emitted through the optically active substance.
Q.What is Bi-quartz device?
A.It consists of two semicircular disc of right handed and left handed quartz which are cemented together to form a circular disc.
Bi-quartz polarimeter
Share this:
15 thoughts on “ bi-quartz polarimeter ”.
plz upload the viva questions related to magnetic susceptbility & fresnel biprism experiment
Thano you! It was helpful Please upload questions / answers of other practicals also Magnetic variation , sonometer bridge , flywheel etc
Thank you ……..from g.kumarswami Please upload more viva questions on polarimeter
this is very helpful… liked it. thanks for ur efforts…
Upload more ques
vry helpful..thnx for this info
It was very much useful……
Very useful
Thankyou so much for helping us. please upload more questions and answers related to other experiment like diffraction grating ,climping and clampin
Thankyou so much for helping us. please upload more questions and answers related to other experiment like diffraction grating ,clipping and clamping.
Plz update questions on lcr experiment.
Coming Soon…
The quality is good but the quantity is less.
Thanks a lot. Do publish questions for other experiments like fly wheel, angle of prism, platinum resistance thermometer, dispersive power, newton rings, diode laser, Carey Foster bridge, magnetic variation 👍🏻👍🏻
Thankyou very much sir
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Website Powered by WordPress.com .
An ongoing discussion about SAP infrastructure
Ideas for Life
Life unfolds through a myriad of experiences, a harmonious blend of highs and lows beckoning for your insight. Immerse yourself in the depths of introspective poems and tales awaiting your discovery here.

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
25+ Interview Questions on Polarimeter?
P olarimetric methods are reliable and simple methods for determining and analyzing the structure of expensive and nonreplicable samples in macro, semi-micro, and microanalysis.
Pharmaceutical, chemical, essential oil, flavor, and food industries use polarimetry for quality control, process control, and research. This technique is so well established that major pharmaceutical companies, as well as the Food & Drug Administration (FDA), use it to describe many substances.
This blog will cover most of the interview questions on polarimeter .
Interview Questions on Polarimeter:
Q1: What is the USP general chapter number for Polarimeter?
A: USP <781> Optical Rotation.
Q2: What is the Definition of a Polarimeter?
A: A device for measuring the polarization of light, and especially (in chemical analysis) for determining the effect of a substance on rotating the plane of polarization of light. Or Especially when used with liquids, the polariscope measures the amount of rotation of the plane of polarization.
Q3: What is the principle of a Polarimeter?
A: A polarimeter measures the rotation of polarized light as it passes through an optically active fluid. Calculating the value of solution concentrations can be done using the measured rotations, especially when dealing with sugars, peptides, and volatile oils.
Q4: What is the function of the polarimeter?
A: Polarimeters measure the direction of polarisation of light or the rotation of a substance to determine its optical properties.
Q5: Which light source is used in polarimetry?
A: A Sodium lamp is used as a light source in a polarimeter.
Q6: Why is a sodium lamp used in a polarimeter?
A: Due to its monochromatic light and high energy output, sodium light is used for this application.
Q7: How does a polarimeter work?
A: Using a polarimeter, you can determine if a sample contains one or both enantiomers. This instrument includes a light source, polarizer, sample cell, detector, and analyzer.
Q8: What is the purpose of a polarimeter?
A: Polarimeters are devices that measure the polarisation direction of light or the rotation of an optically active substance.
Q9: What is polarimeter instrumentation?
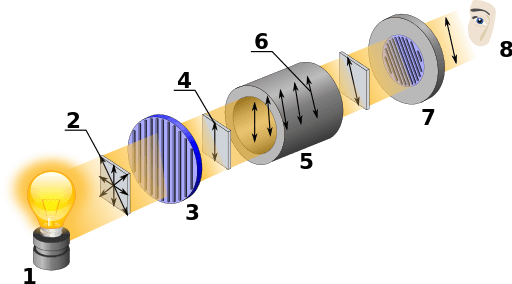
A: A polarimeter consists of;
- light source,
- A monochromator, (filters out all but a specific wavelength of light)
- A polarizer (converts the light beam to plane-polarized light),
- A sample tube (holds the sample being measured),
- A second polarizer (to determine the degree of rotation), and
- A light detector.
Q10: What is D line of Sodium?
A: On the Sodium spectrum, the D-lines are the prominent lines at 588.9950 and 589.5924 nanometers, known as the Sodium D-lines. It can be seen from the energy level diagram that these lines are emitted during a transition from the 3p to the 3s levels. There is twice the intensity of the line at 589.0 nm compared to the line at 589.6 nm.
Q11: Why are some molecules optically active?
A: An enantiomer of a chiral molecule rotates light in a certain direction when plane-polarized light passes through one of the two enantiomers. When the same plane-polarized light is passed through the other enantiomer, that enantiomer rotates light in the opposite direction by the same amount.
The light will rotate counterclockwise for one enantiomer and clockwise for the other. Because chiral molecules can rotate the plane of polarization differently as a result of interacting with an electric field differently, they are known as optically active molecules.
Q12: What are Enantiomers?
A: The Chiral molecule has two mirror images that cannot match perfectly-the mirror images are non-superimposable. The mirror images of a compound are called enantiomers.
Q13: Is glucose optically active?
A: Yes, Due to the chiral centers of four carbon atoms within glucose make it an optically active compound.
Q14: What is a formula for SOR?
A: The formula for SOR is,
OR/(Conc. of Sample x Path length)
α observed
[α] = —————-
where, α = Specific Optical Rotation,
α observed = Optical Rotation,
c = Concentration of sample,
l = Path Length
Q15: What is the length of the polarimeter tube?
A: There is no specific length, it varies from 5 mm to 200mm.
Q16: How do you find the concentration of a polarimeter?
A: Let’s see an example to understand this answer,
For example, if a sample prepared by dissolving 2 g of optical material in water to a final volume of 20 mL and measuring its optical rotation in a 5.0 cm cell was determined to have an optical rotation of +5.5 degrees, then the concentration of the sample 2 g/20 mL = 0.2 g/ml, and, [α] = 5.5/(0.2×5) = 5.5.
Q17: Why sucrose is used for the calibration of the polarimeter?
A: Basically, polarimetry analyzes the angle of rotation of transverse waves (e.g., electromagnetic light), which passes through optically active fluids like sucrose, which is nearly ideal for testing and calibration.
Q18: In calibrating polarimeters, why should sucrose solutions of 10%,20%,30% be used?
A: When we use above 30% concentration, assume we use 40% concentration or more. In such a case, two molecules will be arranged one behind the other, and you will have a minimum optical rotation with respect to actual concentration.
Q19: What is the wavelength of the polarimetry lamp?
A: 589.44nm, Sodium lamp polarimeter.
Q20: What is the value of specific rotation of sugar solution?
A: The value of the specific rotation solution is 0.
Q21: How do you fill a polarimetry tube?
A: A slight incline should be achieved with the tube.
Q22: Which waves can not be polarized?
A: As long as the motion of particles is in one dimension, longitudinal waves cannot be polarized, such as sound waves. Therefore, ultrasonic waves cannot be polarized since they are sound waves.
Q23: What is the use of specific rotation?
A: When producing pharmaceuticals and cosmetics, for instance, specific rotation of products can be a key parameter to control the purity of the optical active ingredients.
Q24: What is the angle of rotation in the polarimeter?
A: An optically active substance is passed through polarized light to measure the angle of rotation. Polarimeters measure this angle.
Q25: What is the advantage of sodium D line light to be used in the polarimeter instead of normal light?
A: Na (Sodium) Lamps produce monochromatic, high-energy light, making them ideal for polarimetry. High sensitivity and signal-to-noise ratio. Monochromatic light is produced by a line spectrum, i.e. at 589nm.
Q26: What is the difference between optically active and inactive?
A: If light moves to the right, then the optical activity is dextrorotatory, and if it moves to the left, then the optical activity is levorotatory. Similarly, if the light stream passes through the Nicol prism, the light is unaffected. As a result, it has been described as optically inactive.
Q27: Why is the plane of polarized light rotated by optically active compounds?
A: An optically active substance has a chiral c – atom. It contains different molecules (group of atoms) attached to it, which will prevent the light from passing through it when it falls on a larger molecule (may be on the left or right side). Like an optical substance, it rotates its path.
Q28: What are dextrorotatory and levorotatory?
A: Compounds that rotate plane-polarized light clockwise (+) are described as dextrorotatory, while those that rotate clockwise (-) are described as levorotatory.
Q29: Which solution is traditionally used for the calibration of polarimeter?
A: The traditional method used to calibrate polarimeters used sugar solutions of a defined concentration with polarimeters relating sugar molecules to light rotation.
Q30: What is the calibration slope?
A: The calibration slope is a conversion factor used by the pH meter to convert electrode signals from mV to pH. The pH meter determines the slope by measuring the difference between two buffers’ mV readings and dividing by the difference in pH.
Q31: Applications of polarimetry in the Pharmaceutical industry?
A: By measuring specific rotation and optical rotation, polarimetry determines product purity:
- Tranquilizers
- Antibiotics
- Amino Sugars
Q32: What is the difference between OR and SOR?
A: The purpose of optical rotation and specific rotation is the same: rotating plane-polarized light into different directions by means of certain substances. They are called optical isomers or enantiomers.
An optical rotation happens when light beams are directed through certain materials and plane-polarized light rotates.
A specific rotation describes the angle of rotation of plane-polarized light by a certain compound at a specific temperature.
Standard rotation measurements for optical rotation for specific chemical compounds are known as specific rotations.

Image Source: Rudolphresearch.com
I hope you found the all types of interview questions on polarimeter. This article may help you to answer the interview.
- HPLC Interview Question and Answers
- Gas Chromatography Interview questions and answers
- Karl Fischer Titration Interview Question and Answer
- Dissolution Interview Question and Answer
- What is Annual Product Quality Review (APQR)?
- What Is Change Control In pharma?
- CAPA Process in Pharmaceutical Management System
- FAQ’s On FDA’s Data Integrity
YT channel: Pharmabeejpro

- Electronics
- Computer Science
- Knowledge Base
- Polarization of Light Interview Question with Answer
Polarization of Light Questions and Answers for Viva
Embark on an illuminating journey into the science of light polarization with our curated collection of Interview Questions and Answers. Whether you're a physics aficionado, a student exploring the wonders of optics, or simply curious about the fascinating phenomenon of light polarization, our comprehensive list covers a diverse range of topics. From the basics of polarization to advanced concepts, such as Brewster's angle and polarizers, our expertly crafted responses provide valuable insights and knowledge. Dive into our repository of interview questions to deepen your understanding of light polarization and impress your friends, colleagues, or interviewers with your newfound expertise. Explore the intriguing properties and applications of polarized light, and uncover the captivating facts and theories that illuminate this intriguing field of study.
Frequently asked questions and answers of Polarization of Light in Optics of Physics to enhance your skills, knowledge on the selected topic. We have compiled the best Polarization of Light Interview question and answer, trivia quiz, mcq questions, viva question, quizzes to prepare. Download Polarization of Light FAQs in PDF form online for academic course, jobs preparations and for certification exams .
Intervew Quizz is an online portal with frequently asked interview, viva and trivia questions and answers on various subjects, topics of kids, school, engineering students, medical aspirants, business management academics and software professionals.
Interview Question and Answer of Polarization of Light
Question-1. State Malus law
Answer-1: When two pieces of Polaroid are placed in succession along the path of a light wave, the intensity of light received behind the two Polaroids is described by Malus’ Law. The law expresses light intensity, I, as a function of the angle which is the angle θ between the directions of polarization of the two filters. The law can be expressed as follows:
I = Imaxcos2 θ
where, Imax is the light intensity between the two sheets of Polaroid.
Question-2. What is meant by Plane Polarization?
Answer-2: Plane polarization is a type of polarization which allows waves to oscillate in only one plane.
Question-3. What is polarization of light?
Answer-3: The light which has acquired the property of one sidedness is called a polarized light.
Question-4. What is Circular polarization?
Answer-4: Circular polarization of an electromagnetic wave is a polarization in which the electric field of the passing wave does not change strength but only changes direction in a rotary manner.
Question-5. What types of waves may be polarized?
Answer-5: Transverse can be polarized as polarization is a property of th transverse waves.
Question-6. What are Dichroic substances
Answer-6: A dichroic material is a crystalline substance in which two preferred states of light polarization are propagated with different velocities, and more importantly, with different absorption.
Question-7. Define Dichroism
Answer-7: Dichroism has two related but distinct meanings in optics. A dichroic material is either one which causes visible light to be split up into distinct beams of different wavelengths (colours) (not to be confused with dispersion), or one in which light rays having different polarizations are absorbed by different amounts.
Question-8. Other than using a polarizing filter, give one way in which visible light may be polarized?
Answer-8: Visible light can be polarized on reflection.
Question-9. Distinguish between unpolarized and plane polarized light?
Answer-9: The unpolarized light is symmetrical about the direction of propagation while in case of plane polarized light, there is lack of symmetry about the direction of propagation.
Question-10. What is polaroid device
Answer-10: Polaroid is a device to produce plane polarized light. It consists of ultra - microscopic crystals of quinine iodo sulphate which are embedded in nitro - cellulose films in such a way that their optic axes are parallel to each other.
Question-11. For what kind of light does malus law hold?
Answer-11: Malus law is completely applicable for completely plane polarized light.
Question-12. Define plane of vibration and plane of polarization
Answer-12: The plane containing the direction of vibration as well as the direction of the propagation of light is called plane of vibration. On the other hand, the plane passing through the direction of propagation and containing no vibration is called plane of polarization.
Question-13. what is the use of photo detector
Answer-13: Photo Detector is an optical detector that converts light signals into electrical signals, which can then be amplified and processed. The photo detector is as essential an element of any fiber optic system as the optical fiber or the light source.
Question-14. What is the use of Polarizer?
Answer-14: Polarizer is an optical filter that passes light of a specific polarization and blocks waves of other polarizations. It can convert a beam of light of undefined or mixed polarization into a beam with well-defined polarization.
Question-15. What do you mean by plane of polarization
Answer-15: The plane of polarization of linearly polarized light or other electromagnetic radiation is the plane containing the electric vectors of the vibrations.
Question-16. Define plane of vibration and plane of polarization
Answer-16: The plane containing the direction of vibration as well as the direction of the propagation of light is called plane of vibration. On the other hand, the plane passing through the direction of propagation and containing no vibration is called plane of polarization.
Question-17. How does polarized light differ from ordinary light?
Answer-17: The ordinary light is symmetrical about the direction of propagation while in case of polarized light, there is lack of symmetry about the direction of propagation.
Frequently Asked Question and Answer on Polarization of Light
Polarization of Light Interview Questions and Answers in PDF form Online
Polarization of Light Questions with Answers
Polarization of Light Trivia MCQ Quiz

Related Topics
- Polarization of Light
- Diffraction Grating
- Resonance Tube
- Ultrasonic Interferometer
- Spectrometer Grating
- Dispersive Power of Prism
- Cauchy's Constants
- Nodal Slide Experiment
- Fresnels Biprism Experiment
More Subjects
- Electicity and Magnetism
- Physics Lab Instruments
All Categories
- Electronics Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- General Knowledge
Can't Find Your Question?
- High School
- You don't have any recent items yet.
- You don't have any courses yet.
- You don't have any books yet.
- You don't have any Studylists yet.
- Information

Viva Voice Applied Physics Final PH-122
Physics (ph-201), nadirshaw eduljee dinshaw university of engineering and technology, recommended for you, students also viewed.
- NED PHYSICS RECREATION PAPER FOR UNIVERSITY STUDENTS
- Experiment 03-rejector-circuit compress
- (FESW) Assignment 1
- Zaamina - practical
- Magnetism and Electromagnetism (F) QP
- Static electricity - practical
Related documents
- Assignment (AP)
- Higher Order PDE - Notes by Kashish Karera
- Classical mechanic - Notes by Kashish Karera
- Assignment # 1
- Important OF TI-WPS Office
- Heat PHY2104 lab manual 2020
Preview text
Www.aminotes.
EXPERIMENT 1 To determine the wavelength of sodium light by Newtons’s rings method.
Q1. What are Newton’s rings? Why they are circular in shape?
Ans. Newton's rings is a phenomenon in which an interference pattern is created by the reflection of light between two surfaces a spherical surface and an adjacent touching flat surface (glass plate).
They are circular because the experiment is usually done with a flat mirror, and a spherical lens; neither of these changes the situation for the light if we rotate them, so the resulting light pattern cannot change. The only patterns that do not change if we rotate them have circular symmetry, so the rings are circular.
Q2. What type of source is used to observe Newton's ring?
Ans A monochromatic source of light is used in it.
Q3. What if the glass plate is replaced with plane mirror?
Ans. Then we will not get interference fringe because the intensity of light reflected from mirror will be so great that it won t be visible and we will get uniform illumination.
Q4. Why do rings get closer as their order increases?
Ans. The diameter of dark rings is proportional to the square root of natural numbers while bright rings are proportional to the square root of odd natural numbers hence the don t increase at the same rate.
Q5. Why is an extended source used in newtons ring experiment?
Ans. Extended source is required to get nearly parallel rays of light
Q6. Explain interference. Ans. The phenomenon in which alternate bright and dark fringes are observed due to the superposition of light waves proceeding from two coherent sources of light.
Q7. Can the experiment be performed in white light? Ans Yes. When viewed with white light, it forms a concentric ring pattern of rainbow colors. Q8. what is the function of the 45° inclined glass plate? A turns the light rays coming from an extended source to ninety degrees and so the rays fall normally on the plano convex lens.
> 1. A ray of light is deflected twice in a prism. The sum of these deflections is the deviation angle. When the entrance and exit angles are equal, t he deviation angle of a ray passing through a prism will be a minimum.
Can a source of monochromatic light be used in this experiment? Ans. No, monochromatic source cannot be used in dispersive power experiment.
Which source of light you are using? Ans. Mercury vapour lamp.
Why two verniers are provided? Ans. So that error can be eliminated.
EXPERIMENT 2
- To determine the dispersive power of the material of prism with the help of a spectrometer.
1)What is polarization and what is the nature of light? Ans. Polarization (also polarisation) is a parameter applying to waves that specifies the geometrical orientation of the oscillation. Electromagnetic waves such as light exhibit multiple polarizations, as do many other types of waves such as gravitational waves and sound waves in solids. Light is a transverse, electromagnetic wave that can be seen by humans. The wavenature of light was first illustrated through experiments on diffraction and interference. Like all electromagnetic waves, light can travel through a vacuum.
how does polarized light differ from ordinary light? Ans. is the direction of oscillation of the electric field in an EM wave. Ordinary (unpolarized) light has random polarization, meaning it will have statistically equal components of polarization in any direction. Polarized light has coherent polarization, meaning the polarization is in one constant direction for the light (polarization can be linear, circular, or elliptical). Light can be partially polarized as well.
define plane of vibration and plane of polarization? Ans. plane in which electromagnetic radiation vibrates when it is polarized so as to vibrate in a single plane is called plane of vibration.
EXPERIMENT 3 • To determine the specific rotation of sugar by Bi-quartz or Laurent half shade polarimeter.
define optical axis and principal section of a birefringence crystal? Ans. a line passing through the centre of curvature of a lens or spherical mirror and parallel to the axis of symmetry is called optical axis. Birefringence is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction oflight.[1] These optically anisotropic materials are said to be birefringent (or birefractive). The birefringence is often quantified as the maximum difference between refractive indices exhibited by the material. Crystals with non-cubic crystal structures are often birefringent, as are plastics under mechanical stress.
what type of polarizer used in the polarimeter you are using? Ans. types of polarimeters are generally used in the laboratory now a days: (a) Laurent’s Half Shade Polarimeter (b) Biquartz Polarimeter
8)what is half shade polarimeter? Ans. is a half shade device which divides the field of polarised light emerging out of the Nicol P into two halves generally of unequal brightness. T is a glass tube in which optically active solution is filled. 9)what is bi-quartz polarimeter? Ans.. consists of two semicircular disc of right handed and left handed quartz which are cemented together to form a circular disc.
1)Define fraunhoffer diffraction? How is it different from fresnal diffraction? Ans optics, the Fraunhofer diffraction equation is used to model thediffraction of waves when the diffraction pattern is viewed at a long distance from the diffracting object, and also when it is viewed at the focal plane of an imaging lens. On the other hand, Fresnel diffraction or near-fielddiffraction is a process of diffraction that occurs when a wave passes through an aperture and diffracts in the near field, causing any diffraction pattern observed to differ in size and shape, depending on the distance between the aperture and the projection.
2)what are the differences between diffraction pattern and interference pattern?
- Two separate wave fronts originating from two coherent sources produce interference. Secondary wavelets originating from different parts of the same wave front constitute diffraction. Thus the two are entirely different in nature.
- The region of minimum intensity is perfectly dark in interference. In diffraction they are not perfectly dark.
- Width of the fringes is equal in interference. In diffraction they are never equal.
- The intensity of all positions of maxima are of the same intensity in interference. In diffraction they do vary.
EXPERIMENT 4
To determine the width of a narrow slit using diffraction phenomena.
Q1. What do you understand by term thermometer?
Ans. An instrument for measuring temperature, especially one having a graduated glass tube with a bulb containing a liquid, typically mercury or colored alcohol, that expands and rises in the tube as the temperature increases.
Q2. Why platinum is used in platinum resistance thermometer experiment?
Ans. Platinum resistance thermometer requires a small current to pass through it to determine its resistance at different temperatures. Platinum has a linear resistance-temperature relationship; can use this method to find the resistance at different temperatures.
Q3. Explain the working principle of platinum resistance wire. Ans. The platinum resistance thermometer-in which the principle of measurement is the variation in the resistance of a platinum wire as a function of temperature-is generally accepted as the most accurate temperature measuring instrument available.
Q4. Define temperature coefficient of resistance. Ans. The resistance-change factor per degree Celsius of temperature
EXPERIMENT 5
To determine the temperature coefficient of platinum wire, using a platinum resistance thermometer and a Callender&Griffth’s bridge
change is called the temperature coefficient of resistance. This factor is represented by the Greek lower-case letter “alpha” (α).
Q5. how resistance depend on temperature? Ans. Resistivity and resistance depend on temperature with the dependence being linear for small temperature changes and nonlinear for large.
- Define specific resistance with unit.
Ans. Specific resistance is the inherent property of a material. It is defined as the resistance offered by a unit length and unit cross sectional area of that material when known voltage is applied at its ends. Its unit is ohm-meter.
- Under what conditions the galvanometer’s deflection will be zero?
Ans. The deflection will be zero when the voltage on both the terminal is same.
- Why the resistance for inner ratio arms be equal?
Ans. For increased sensitivity and accuracy.
- What is the change in specific resistance if radius or length of wire is changed?
Ans. It is independent of length or radius of wire and only depends on the material of wire.
EXPERIMENT 6
To determine the resistance per unit length of a Carey Foster’s bridge wire and also to find out the specific resistance of a given wire.
- What is simple pendulum? What is the advantage of compound pendulum over simple pendulum?
Ans. A device consisting of a small massive body suspended by an inextensible object of negligible mass from a fixed horizontal axis about which the body and suspension are free to rotate. Simple pendulum is an ideal pendulum because it needs a point mass suspended by weightless string which makes it ideal, whereas there is no such condition for compound pendulum and hence errors involving in measurement of (g) with the pendulum reduces.
- What is meant by the acceleration due to gravity? What is its unit?
Ans. The acceleration gained by an object because of gravitational force is called its acceleration due to gravity. Its unit is m/s2.
- What is the difference between ‘G’ and ‘g’?
Ans. G stands for Newton’s universal gravitational constant, whereas g stands for the acceleration due to gravity.
- What is radius of gyration? Ans. It is defined as the distance from axis of rotation to a point
EXPERIMENT 8
To determine the value of acceleration due to gravity (“g”) in the laboratory using bar pendulum.
1 a Sonometer. How it can be used to find the frequency of the given tuning fork?
Ans: A sonometer is a device used for studying transverse vibrations of a string. The frequency of the tuning fork is determined by using a sonometer and a paper rider utilising the resonance phenomenon. n = (1/2l)x
2 is the significance of the u shape of the tuning fork?
Ans: U-shaped fork produces a much purer tone than other shaped resonators. Secondarily, when struck, the fundamental frequency of vibration has the two sides of the fork move alternately towards and away from each other.
3 frequency and give its unit?
Ans:The frequency of a wave is the number of waves passing a point in a certain time Unit of frequency is the hertz(Hz)
EXPERIMENT 10
To determine the density of material of the given wire with the help of Sonometer
4 is the function of the holes in the wooden box?
Ans:The holes in the sonometer box provides a way so that vibrations from the tuning fork (which is excited near the sonometer) is transferred to the inside of the sonometer box. Thus, the sonometer box, the bridges and the string are forced to vibrate with the frequency of the tuning fork.
- How Sonometer is similar to other stringed musical instruments?
Ans: Sonometer and other stringed musical instruments are based on the Phenomenon of Resonance.
- Discuss the formation of stationary waves in the Sonometer?
Ans: Stationary waves are formed when two progressive waves with the same frequency and similar amplitudes, travelling in opposite directions, interfere with each other.
7 is resonance? When does resonance occur in the Sonometer? Ans: Resonance is a phenomenon in which a vibrating system or external force drives another system to oscillate with greater amplitude at a specific preferential frequency.
- Multiple Choice
Course : Physics (PH-201)
University : nadirshaw eduljee dinshaw university of engineering and technology.

- Discover more from: Physics PH-201 Nadirshaw Eduljee Dinshaw University of Engineering and Technology 48 Documents Go to course
- More from: Physics PH-201 Nadirshaw Eduljee Dinshaw University of Engineering and Technology 48 Documents Go to course
To determine the specific rotation of a sugar using a polarimeter
In this experiment, the user will prepare a sugar solution of known concentration (c), but unknown identity. The user will obtain the observed rotation (αobs) from the experiment using the polarimeter and use that information to calculate the specific rotation [α] of the given sample using the above formula. The identity of the sample can thus be found out from the given list of specific rotations for different chemicals.
The procedure to perform this experiment is self-explanatory and leads the user in a step-by step manner to accomplish the task. The protocol briefly involves the following steps:
User will click on the virtual lab link (simulator).
To know details regarding the instrumentation of the polarimeter.
i. Click on "Know Your Polarimeter" option. ii. Click on the Polarimeter to Zoom-in as indicated by an arrow. iii. Click on the red button provided to switch on the polarimeter and to see the light source in the polarimeter instrument. iv. Click on the panel indicated by arrow to open the sample chamber. v. After you see 100% Intensity of the light coming through the eye piece at α 20 D then click Continue. vi. Click on the button "click to record experiment without login" to perform an experiment and further follow instructions as detailed in step 3.
To directly perform an experiment using the polarimeter.
i. Click on any of the 6 sugar sample in the bottles on the shelves. ii. Type in the amount of sugar (in gm/100mL) that you want to use for the experiment in the text box provided and then presses enter on the keyboard. iii. Click on one of the sample cells to transfer the prepared sugar solution into a cell of particular path length. iv. After transferring the contents into the sample cell, click on the sample cell to place it into the polarimeter's sample chamber. v. Click on the power button to switch on the polarimeter to record the optical rotation of the sample. vi. To rotate the dial of the eye piece in clockwise direction click on '+' button and for anticlockwise direction click on '-' button. vii. To change the Increment Factor click on the IF* buttons 1, 5 or 10 accordingly. viii. Rotate the dial both in clockwise and anti-clockwise directions for the whole 360o until you see a maximum light intensity in the right semicircle, matching the left semicircle exactly. ix. Click on open record form and note down all the 4 different αobs angles where you observed maximum Intensity.
- Estimate the specific rotation [α] using the equation for liquids.
- Compare the obtained specific rotation [α] value against the table provided below to identify the identity of the sugar used in the experiment.
- Click on save form and perform calculations and choose the appropriate identity of the unknown sugar you have used in the experiment.
- Either click on "Click to restart the experiment" and follow the instructions from step 3 or "Click to try with same sample sugar" and follow the instructions from step 3, substep (ii).
* NOTE: While doing the experiments you will notice that if the maximum intensity of light is observed at x° degree, it is also observed at (180+ x)° degree. From a single experiment, it is not possible to infer which the value for total rotation αtotal actually is. Then again, the observation only tells us about the orientation of the plane of polarization of the emergent light relative to that of the incident light. However, one can not off hand say anything about what is the actual total rotation the plane has undergone. Thus, for example, the observation of maxima at x° and at (180 + x)° may mean that the value of αtotal could also be (360n + x) °; where n = 0, 1, 2, … Similarly, it could also be that αtotal is -(360 - x)° or –(360 - (180 + x))° depending on whether the rotation of the light has taken place in the anticlockwise or clockwise direction. For example if the maximum intensity is observed at α value of 30° and 210° , then could be any one of the values: 30°, 210°, -330°, -150° or even 7390° or 570°. To confirm the actual value of αtotal, one needs to repeat the experiment using different concentration and variable path lengths. Though there would be an ambiguity regarding the αtotal for each of these experiments, the correct choices would provide the same specific rotation [α] T λ or [α] 20 D
Sample data for the experiment

IMAGES
COMMENTS
This document contains 24 questions and answers about the polarimeter experiment. Key points covered include: 1) Light waves are transverse electromagnetic waves, with the electric field component playing the role of light. Polarized light has a transverse electric vector in a specific direction, while ordinary light vibrates in all directions. 2) Nicol prisms and polaroids can produce ...
Q. 22. What is a polarimeter ? Ans. Polarimeter is a device used for the measurement of optical rotation and the angle ofrotation of the plane of polarisation rotated by an optically active substance. Q. 23 What are the main parts of a polarimeter ? Ans. The main parts of a polarimeter are; a polariser, an analyser and a polarimeter tube (or glass
Feb 17, 2015 · UÁ0Rwå®“Ú H Uµ vˆÈI« @UµN nª „Ÿ~ùí ¿þùï? Ç |˜–í¸žÏïÿý5ÿÿ»ýù¢y« ·ÌŽµ—s^kµ“Sµóñ¬® Œ†„&AA¯÷Kí½çršß"; ¼€Šåù½mú Ic™5 þ ¹¤üé^ÿ« ¦:W»ƒÐC&€ÿâ*Œïçósü ! › ÂNb3³U¹ÕVÅVåþ¯Ëª 'Ñ êMÓý¶d$¸]6=Çuû}Ð ¨ + W{ ƒh'É7›0Ú-_í+ÖO¢·ÎPB£a¹Þ}£uç¦Ð ´È ‰Ô’ÒÌêLz•_ „÷¿ïoý ËÏ ...
#vivavideo #viva #physics #practical In this video lecture, viva question of specific rotation of cane sugar practical is discussed. hope you all like it.
A: A Sodium lamp is used as a light source in a polarimeter. Q6: Why is a sodium lamp used in a polarimeter? A: Due to its monochromatic light and high energy output, sodium light is used for this application. Q7: How does a polarimeter work? A: Using a polarimeter, you can determine if a sample contains one or both enantiomers.
down to view a list of all Viva Questions based on Polarimeter/Specific Rotation Experiment. We have concluded a list of viva questions based on Polarimeter/Specific Rotation asking in examination and practical lab.1. What is Polarimeter? Ans : It is a device used to measure the angle of rotation of plane of polarization rotated by an optically ...
Polarization of Light Questions and Answers for Viva Embark on an illuminating journey into the science of light polarization with our curated collection of Interview Questions and Answers. Whether you're a physics aficionado, a student exploring the wonders of optics, or simply curious about the fascinating phenomenon of light polarization ...
Physics lab: Viva-Voce Question and Answers 1. Series and Parallel resonance. What is an inductor? A: An inductor is a passive component used to store energy in the form of a magnetic field. Define resistance? A: The opposition offered to the flow of D. by a component in a circuit is called resistance.
EXPERIMENT 3 • To determine the specific rotation of sugar by Bi-quartz or Laurent half shade polarimeter. WWW.AMINOTES. define optical axis and principal section of a birefringence crystal? Ans. a line passing through the centre of curvature of a lens or spherical mirror and parallel to the axis of symmetry is called optical axis.
The procedure to perform this experiment is self-explanatory and leads the user in a step-by step manner to accomplish the task. The protocol briefly involves the following steps: User will click on the virtual lab link (simulator). To know details regarding the instrumentation of the polarimeter. i. Click on "Know Your Polarimeter" option. ii.