Press ESC to close
Or check our popular categories..., branch and bound | set 4 (job assignment problem).
Let there be N workers and N jobs. Any worker can be assigned to perform any job, incurring some cost that may vary depending on the work-job assignment. It is required to perform all jobs by assigning exactly one worker to each job and exactly one job to each agent in such a way that the total cost of the assignment is minimized.
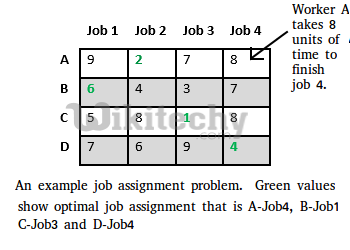
Let us explore all approaches for this problem.
Solution 1: Brute Force We generate n! possible job assignments and for each such assignment, we compute its total cost and return the less expensive assignment. Since the solution is a permutation of the n jobs, its complexity is O(n!).
Solution 2: Hungarian Algorithm The optimal assignment can be found using the Hungarian algorithm. The Hungarian algorithm has worst case run-time complexity of O(n^3).
Solution 3: DFS/BFS on state space tree A state space tree is a N-ary tree with property that any path from root to leaf node holds one of many solutions to given problem. We can perform depth-first search on state space tree and but successive moves can take us away from the goal rather than bringing closer. The search of state space tree follows leftmost path from the root regardless of initial state. An answer node may never be found in this approach. We can also perform a Breadth-first search on state space tree. But no matter what the initial state is, the algorithm attempts the same sequence of moves like DFS.
Solution 4: Finding Optimal Solution using Branch and Bound The selection rule for the next node in BFS and DFS is “blind”. i.e. the selection rule does not give any preference to a node that has a very good chance of getting the search to an answer node quickly. The search for an optimal solution can often be speeded by using an “intelligent” ranking function, also called an approximate cost function to avoid searching in sub-trees that do not contain an optimal solution. It is similar to BFS-like search but with one major optimization. Instead of following FIFO order, we choose a live node with least cost. We may not get optimal solution by following node with least promising cost, but it will provide very good chance of getting the search to an answer node quickly.
There are two approaches to calculate the cost function:
- For each worker, we choose job with minimum cost from list of unassigned jobs (take minimum entry from each row).
- For each job, we choose a worker with lowest cost for that job from list of unassigned workers (take minimum entry from each column).
In this article, the first approach is followed.
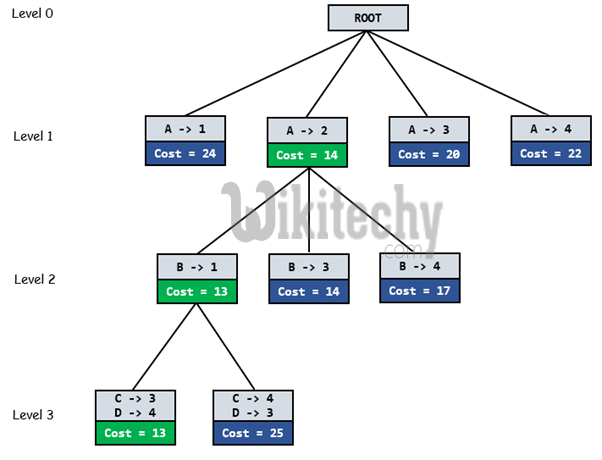
Let’s take below example and try to calculate promising cost when Job 2 is assigned to worker A.
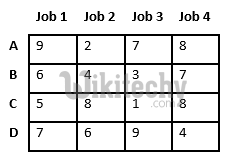
Since Job 2 is assigned to worker A (marked in green), cost becomes 2 and Job 2 and worker A becomes unavailable (marked in red).
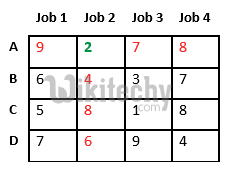
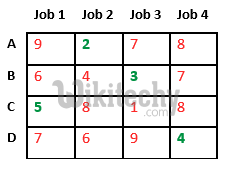
Now we assign job 3 to worker B as it has minimum cost from list of unassigned jobs. Cost becomes 2 + 3 = 5 and Job 3 and worker B also becomes unavailable.

Finally, job 1 gets assigned to worker C as it has minimum cost among unassigned jobs and job 4 gets assigned to worker C as it is only Job left. Total cost becomes 2 + 3 + 5 + 4 = 14.
Below diagram shows complete search space diagram showing optimal solution path in green.
Complete Algorithm:
Below is its C++ implementation.
Categorized in:
Share Article:

Venkatesan Prabu
Wikitechy Founder, Author, International Speaker, and Job Consultant. My role as the CEO of Wikitechy, I help businesses build their next generation digital platforms and help with their product innovation and growth strategy. I'm a frequent speaker at tech conferences and events.
Leave a Reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related Articles
10 steps to quickly learn programming in c#, c program print bst keys in the given range, java program print bst keys in the given range, cpp algorithm – length of the longest valid substring, other stories, c programming – inserting a node in linked list | set 2, c++ program check if a number is multiple of 9 using bitwise operators, summer offline internship.
- Internship for cse students
- Internship for it students
- Internship for ece students
- Internship for eee students
- Internship for mechanical engineering students
- Internship for aeronautical engineering students
- Internship for civil engineering students
- Internship for bcom students
- Internship for mcom students
- Internship for bca students
- Internship for mca students
- Internship for biotechnology students
- Internship for biomedical engineering students
- Internship for bsc students
- Internship for msc students
- Internship for bba students
- Internship for mba students
Summer Online Internship
- Online internship for cse students
- Online internship for ece students
- Online internship for eee students
- Online internship for it students
- Online internship for mechanical engineering students
- Online internship for aeronautical engineering students
- Online internship for civil engineering students
- Online internship for bcom students
- Online internship for mcom students
- Online internship for bca students
- Online internship for mca students
- Online internship for biotechnology students
- Online internship for biomedical engineering students
- Online internship for bsc students
- Online internship for msc students
- Online internship for bba students
- Online internship for mba students
Internship in Chennai
- Intenship in Chennai
- Intenship in Chennai for CSE Students
- Internship in Chennai for IT Students
- Internship in Chennai for ECE Students
- Internship in Chennai for EEE Students
- Internship in Chennai for EIE Students
- Internship in Chennai for MECH Students
- Internship in Chennai for CIVIL Students
- Internship in Chennai for BIOTECH Students
- Internship in Chennai for AERO Students
- Internship in Chennai for BBA Students
- Internship in Chennai for MBA Students
- Internship in Chennai for MBA HR Students
- Internship in Chennai for B.Sc Students
- Internship in Chennai for M.Sc Students
- Internship in Chennai for BCA Students
- Internship in Chennai for MCA Students
- Internship in Chennai for B.Com Students
- Internship in Chennai for M.Com Students
Programming / Technology Internship in Chennai
- Data Science Internship in Chennai
- Artificial Intelligence Internship in Chennai
- Web Development Internship in Chennai
- Android Internship in Chennai
- Cloud Computing Internship in Chennai
- .Net Internship in Chennai
- JAVA Internship in Chennai
- Ethical Hacking Internship in Chennai
- IOT Internship in Chennai
- Machine Learning Internship in Chennai
- Networking Internship in Chennai
- Robotics Internship in Chennai
- Matlab Internship in Chennai
Navigation Menu
Search code, repositories, users, issues, pull requests..., provide feedback.
We read every piece of feedback, and take your input very seriously.

Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly.
To see all available qualifiers, see our documentation .
- Notifications You must be signed in to change notification settings
Solved the Job Assignment Problem using a branch and bound algorithm
Valor-boop/Job-Assignment-Problem
Folders and files, repository files navigation, job-assignment-problem.
Solved the Job Assignment Problem using both brute force as well as branch and bound. The code contains 5 functions:
job_assignment(cost_matrix): Find an optimal solution to the job assignment problem using branch and bound. Input: an nxn matrix where a row represents a person and a column represents the cost each person takes to complete the jobs. Return: the minimal cost, an optimal solution, and the number of partial or full solutions evaluated.
get_csf(cost_matrix, partial_solution): Input: an nxn cost matrix and a partial solution. Return: the partial solution's Cost So Far (CSF). A partial solution is represented as a list of n elements, where an undecided element is denoted by a -1. For instance, a partial solution [2, -1, -1] represents assigning job 2 to person 0 and leaving the assignments of person 1 and person 2 undecided.
get_gfc(cost_matrix, partial_solution): Input: an nxn cost matrix and a partial solution. Return: the partial solution's Guaranteed Future Cost (GFC).
get_ffc(cost_matrix, partial_solution): Input: an nxn cost matrix and a partial solution. Return: the partial solution's Feasible Futre Cost (FFC)
brute_force(cost_matrix): This function finds an optimal solution for the job assignment problem using brute force. Input: an nxn cost matrix. Return: the minimal total cost, an optimal solution, and the number of full solutions investigated.
- Python 100.0%
- For educators
- English (US)
- English (India)
- English (UK)
- Greek Alphabet
This problem has been solved!
You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts.
Question: Implement a C program for Job assignment problem using LC-branch and bound technique which does the task of assigning a given set of jobs to a given set of persons in such a way that the overall execution time of the task is reduced. The cost matrix for the same is given below. job 1 job 2 9 2 6 4 5 8 7 6 job 3 job 4 3 7 8 3 7 C= person a person b person c

1. Initialization:
1.1. Start from the source node (initial city or person). 1.2. Calculate ...
Not the question you’re looking for?
Post any question and get expert help quickly.
- Data Science
- Trending Now
- Data Structures
- System Design
- Foundational Courses
- Practice Problem
- Machine Learning
- Data Science Using Python
- Web Development
- Web Browser
- Design Patterns
- Software Development
- Product Management
- Programming
Job assignment Problem | DSA Problem
Delve into the complexities of the job assignment problem and master an effective solution using the branch and bound technique with our detailed programming tutorial. This guide is essential for operations researchers, algorithm designers, and computer science students who are keen to understand and implement optimization algorithms in real-world scenarios.
In this tutorial, you'll learn:
- The fundamentals of the job assignment problem and its significance in operations research and resource management.
- An introduction to the branch and bound algorithm as a powerful tool for solving optimization problems by systematically enumerating candidate solutions.
- Step-by-step coding demonstrations that explain how to apply branch and bound to the job assignment problem, ensuring you grasp the methodology and can implement it effectively.
- Practical examples that illustrate the process and show the algorithm in action, helping you see the optimization in real-time.
- Optimization strategies and best practices to enhance the efficiency of your solutions, crucial for handling complex scenarios in professional environments.
By the end of this video, you’ll have a robust understanding of using branch and bound to solve optimization problems, equipping you with skills that are highly valued in industries like logistics, software development, and systems engineering.
For a deeper dive into this topic, including detailed code snippets and a more thorough discussion on branch and bound techniques, please visit our full article: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/job-assignment-problem-using-branch-and-bound/


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Branch and bound algorithms are used to find the optimal solution for combinatory, discrete, and general mathematical optimization problems. A branch and bound algorithm provide an optimal solution to an NP-Hard problem by exploring the entire search space. Through the exploration of the entire sear
Branch And Bound (Job Assignment Problem) - Branch And Bound - It is required to perform all jobs by assigning exactly one worker to each job. ... // Program to solve Job Assignment problem // using Branch and Bound #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; ...
incurring some cost that may vary depending on the work-job assignment. It is required to perform all jobs by assigning exactly one worker to each job and exactly one job to each agent in such a way that the total cost of the assignment is minimized ...
Question: Write a C PROGRAM to implement job assignment problem using BRANCH AND BOUND TECHNIQUE. NOTE: Write program ONLY IN C LANGUAGE, and follow BRANCH AND BOUND TECHNIQUE ONLY Give SCREENSHOT of SAMPLE RUN for the input given below ... Write a C PROGRAM to implement job assignment problem using BRANCH AND BOUND TECHNIQUE. NOTE: Write ...
Job Assignment Problem using Branch And Bound; Travelling Salesman Problem (TSP) using Reduced Matrix Method; Generate Binary Strings of length N using Branch and Bound; ... we can optimize it using Dynamic Programming. The idea is to simply store the results of subproblems so that we do not have to re-compute them when ne.
It is an NP-hard problem. Here is source code of the C Program to Implement Branch and Bound Method to Perform a Combinatorial Search. The C program is successfully compiled and run on a Linux system. The program output is also shown below.
Now let's discuss how to solve the job assignment problem using a branch and bound algorithm. Let's see the pseudocode first: algorithm MinCost(M): // INPUT // M = The cost matrix // OUTPUT // The optimal job assignment minimizing the total cost while true: E <- LeastCost() if E is a leaf node: print(E) return for each child S of E: Add(S) S.parent <- E
Solved the Job Assignment Problem using both brute force as well as branch and bound. The code contains 5 functions: job_assignment(cost_matrix): Find an optimal solution to the job assignment problem using branch and bound. Input: an nxn matrix where a row represents a person and a column represents the cost each person takes to complete the jobs.
Answer to Implement a C program for Job assignment problem. Implement a C program for Job assignment problem using LC-branch and bound technique which does the task of assigning a given set of jobs to a given set of persons in such a way that the overall execution time of the task is reduced.
An introduction to the branch and bound algorithm as a powerful tool for solving optimization problems by systematically enumerating candidate solutions. Step-by-step coding demonstrations that explain how to apply branch and bound to the job assignment problem, ensuring you grasp the methodology and can implement it effectively.