
- Productivity
- Thoughtful learning

Become a better critical thinker with these 7 critical thinking exercises

Critical thinking is a skill you can use in any situation. Whether you're a student, entrepreneur, or business executive, critical thinking can help you make better decisions and solve problems.
But learning critical thinking skills isn't always an easy task. Many tools, techniques, and strategies are available, and choosing the right one can be challenging. Vague suggestions on the internet like "read more" aren't very helpful, and elaborate business examples don’t apply to many of us.
As average problem-solvers, we need actionable thinking exercises to improve our critical thinking skills and enhance our thinking processes. Regularly performing exercises that specifically stretch our decision-making and reasoning skills is the most effective method of improving our thinking abilities.
This article will explore several exercises that will help you develop critical thinking skills. Whether you are preparing for an exam, making an influential decision for your business, or going about your daily life, these fun activities can build your reasoning skills and creative problem-solving abilities.
Boost your logical thinking skills and start practicing a critical mindset with these 10 critical thinking exercises.
A Quick Look at Critical Thinking
As a thoughtful learner, you likely already understand the basics of critical thinking, but here's a quick refresher.
Critical thinking involves analyzing problems or issues objectively and rationally. Critical thinkers are able to understand their own biases and assumptions, as well as those of others. They’re also able to see the world from a different point of view and understand how their experiences impact their thinking.
Developing critical thinking skills is essential because it allows us to see things from multiple perspectives, identify biases and errors in reasoning, and be open to possible solutions. Making informed decisions is easier when we have a better understanding of the world around us.
Why We Need to Practice Critical Thinking

We aren't born with critical thinking skills, and they don’t naturally develop beyond survival-level thinking. To master critical thinking, we must practice it and develop it over time.
However, learning to think critically isn't as easy as learning to ride a bicycle. There aren't any step-by-step procedures to follow or supportive guides to fall back on, and it is not taught in public schools consistently or reliably. To ensure students' success, teachers must know higher-order thinking skills (HOTS) and how to teach them, research says.
Unfortunately, although teachers understand the importance of HOTS and attempt to teach it, studies show that their capacity to measure students' HOTS is low. Educator and author Dr. Kulvarn Atwal says, "It seems that we are becoming successful at producing students who are able to jump through hoops and pass tests."
As critical thinking skills become more important in higher grades, some students find it challenging to understand the concept of critical thinking. To develop necessary thinking skills, we must set aside our assumptions and beliefs. This allows us to explore and question topics from a "blank page" point of view and distinguish fact from opinion.
Be the first to try it out!
We're developing ABLE, a powerful tool for building your personal knowledge, capturing information from the web, conducting research, taking notes, and writing content.
7 Critical Thinking Exercises To Improve Your Critical Thinking Skills

The good news is that by assessing, analyzing, and evaluating our thought processes, we can improve our skills. Critical thinking exercises are key to this improvement. Our critical thinking builds and improves with regular practice, just like a muscle that gets stronger with use.
If you want to become a better critical thinker , here are some critical thinking exercises to try:
Exercise #1: The Ladder of Inference
You can exercise your critical thinking skills by using the Ladder of Inference model . This thinking model was developed by renowned organizational psychologist Chris Argyris. Each rung on the ladder of inference represents a step you take to arrive at your conclusions.
The decision-making process starts when we are faced with a problem or situation. As soon as we observe something problematic or important, we presume what is causing it, and then we use that assumption to draw conclusions. Based on those conclusions, we take action.
For example, say you're at a party and see a friend across the room. You catch their eye and wave, but they turn and walk away. Using the ladder, you might climb the rungs as follows:
- Observe that your friend walked away.
- Select a few details of the situation, including your wave and your assumption that they saw you.
- Meaning is attached based on the environment, making you think your friend must have other people to talk to at the party.
- Assumptions are made based on that meaning, assuming that means your friend doesn’t like you as much as them.
- Conclusions are drawn from the assumption, and you determine that your friend must be mad at you or doesn't want you to be at the party.
- Beliefs are formed, making you think you're not welcome.
- Action is taken, and you leave the party.
In this example, you started with a situation (someone walking away at a crowded party) and made a series of inferences to arrive at a conclusion (that the person is mad at you and doesn't want you there).
The Ladder of Inference can be a helpful tool to frame your thinking because it encourages you to examine each step of your thought process and avoid jumping to conclusions. It's easy to make assumptions without realizing it, as in this scene. Perhaps your friend never even saw you wave from across the crowded room.
Exercise #2: The Five Whys
The "Five Whys" technique is an analytical skill that can help you uncover the source of a problem. The activity was created by Sakichi Toyoda, the founder of Toyota, and consists of repeatedly asking “why?” when a problem is encountered to determine its root cause.
This exercise can be difficult because knowing if you've discovered the source of your problem is challenging. The "five" in "Five Whys" is just a guideline — you may need to ask more. When you can't ask anything else, and your response is related to the original issue, you've probably arrived at the end.
Even if you need several rounds of questioning, just keep going. The important part that helps you practice critical thinking is the process of asking "why?" and uncovering the deeper issues affecting the situation.
For instance, say you're trying to figure out why your computer keeps crashing.
- You ask " why ," and the answer is that there's a software problem.
- Why? Because the computer keeps running out of memory.
- Why? Because too many programs are running at the same time.
- Why? Because too many browser tabs are open .
- Why? Because multitasking is fragmenting your focus, you're doing too many things at once.
In this example, working through the "why's" revealed the underlying cause. As a result, you can find the best solution, which is concentrating on just one thing at a time.
Exercise #3: Inversion

Inversion is another critical thinking exercise that you can use in any situation. Inversion is sort of like taking on the role of the devil's advocate. In this exercise, adopt the opposite view of whatever issue you're exploring and consider the potential arguments for that side. This will help broaden your critical thinking skills and enable you to see other perspectives on a situation or topic more clearly.
For example, let's say you're thinking about starting your own business. Using inversion, you would explore all of the potential arguments for why starting your own business is bad. This might include concerns like:
- You could end up in debt.
- The business might fail.
- It's a lot of work.
- You might not have time for anything else.
By exploring these potentially adverse outcomes, you can identify the potential risks involved in starting your own business and make a more sound decision. You might realize that now is not the right time for you to become an entrepreneur. And if you do start the company, you'll be better prepared to deal with the issues you identified when they occur.
Exercise #4: Argument Mapping
Argument mapping can be a beneficial exercise for enhancing critical thinking skills. Like mind mapping, argument mapping is a method of visually representing an argument's structure. It helps analyze and evaluate ideas as well as develop new ones.
In critical thinking textbooks, argument diagramming is often presented to introduce students to argument constructions. It can be an effective way to build mental templates or schema for argument structures, which researchers think may make critical evaluation easier .
Argument maps typically include the following:
- Conclusion: What is being argued for or against
- Premises: The reasons given to support the conclusion
- Inferences: The connections made between the premises and conclusion
The argument map should be as clear and concise as possible, with a single word or phrase representing each element. This will help you make connections more easily. After the map is completed, you can use it to identify any weak points in the argument. If any areas aren't well-supported, additional premises can be added.
Argument mapping can be applied to any situation that requires critical thinking skills. The more time you take to map out an argument, the better you'll understand how the pieces fit together. Ultimately, this will help you think more creatively and critically, and make more informed decisions.
Exercise #5: Opinion vs. Fact
Critical thinking activities that focus on opinions and facts are particularly valuable and relevant new learning opportunities. Our constantly-connected world makes it easy to confuse opinions and facts , especially with sensationalist news articles and click-bait headlines.
How can you tell a fact from an opinion? Facts are generally objective and established, whereas opinions are subjective and unproven. For example, "the cloud is in the air" is a fact. "That dress looks good on you" is an opinion.
Practice your critical thinking skills by reading or listening to the news. See if you can identify when someone is stating an opinion rather than a fact. Ask yourself the following questions:
- Who is saying what? What reasons might be behind their statements?
- Does the claim make sense? Who would disagree with it and why?
- How can you tell if the data is reliable? Can it be fact-checked? Has it been shared by other credible publishers?
- How do you know whether or not the presenter is biased? What kind of language is being used?
This powerful exercise can train your mind to start asking questions whenever presented with a new claim. This will help you think critically about the information you're taking in and question what you're hearing before accepting it as truth.

Exercise #6: Autonomy of an Object
In her book " The Critical Thinking Tool Kit ," Dr. Marlene Caroselli describes a critical thinking exercise called "Living Problems, Lively Solutions." This exercise uses the autonomy of an object as a problem-solving tool to find a possible solution.
To do this, you'll personify your problem and place it in another context — a different time or place. This allows you to uncover unique solutions to the problem that might be tied to your mental associations with that setting.
For example, if your problem is poor time management , you might personify the issue as a thief of your time. The idea of a thief could make you think of jail, which might prompt thoughts of locking up specific distractions in your life. The idea of jail could also make you think of guards and lead you to the possible solution of checking in with an accountability buddy who can make sure you're sticking to your schedule.
The autonomy-of-object technique works because it stimulates thoughts you wouldn’t have considered without the particular context in which you place the problem.
Exercise #7: The Six Thinking Hats
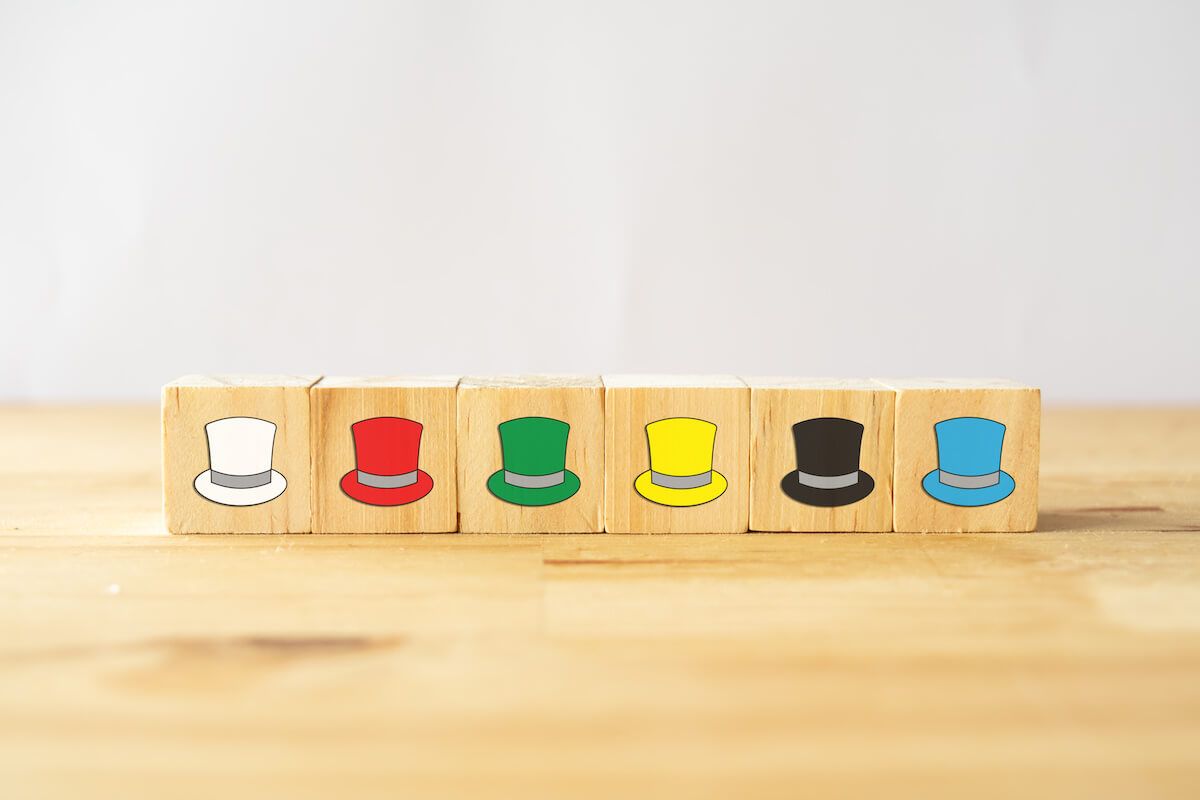

Designed by Edward de Bono, the Six Thinking Hats is a critical thinking exercise that was created as a tool for groups to use when exploring different perspectives on an issue. When people use other thinking processes, meetings can become challenging rather than beneficial.
To help teams work more productively and mindfully, de Bono suggests dividing up different styles of thinking into six categories, represented as hats:
- The white hat is objective and focuses on facts and logic
- The red hat is intuitive, focusing on emotion and instinct
- The black hat is cautious and predicts negative outcomes
- The yellow hat is optimistic and encourages positive outcomes
- The green hat is creative, with numerous ideas and little criticism
- The blue hat is the control hat used for management and organization
With each team member wearing a different hat, a group can examine an issue or problem from many different angles, preventing one viewpoint (or individual) from dominating the meeting or discussion. This means that decisions and solutions reached using the Six Thinking Hats approach will likely be more robust and effective, and everyone’s creative thinking skills will benefit.
Train Your Brain With Critical Thinking Exercises
Using critical thinking regularly in various situations can improve our ability to evaluate and analyze information. These seven critical thinking exercises train your brain for better critical thinking skills . With daily practice, they can become habits that will help you think more critically each day.
Improve your critical thinking with ABLE
Ask better questions and get better answers with ABLEs integrated web search, annotation and note-taking features. Check how ABLE helps you to improve your critical thinking.
I hope you have enjoyed reading this article. Feel free to share, recommend and connect 🙏
Connect with me on Twitter 👉 https://twitter.com/iamborisv
And follow Able's journey on Twitter: https://twitter.com/meet_able
And subscribe to our newsletter to read more valuable articles before it gets published on our blog.
Now we're building a Discord community of like-minded people, and we would be honoured and delighted to see you there.

Straight from the ABLE team: how we work and what we build. Thoughts, learnings, notes, experiences and what really matters.
Read more posts by this author
follow me :
Mental models: 13 thinking tools to boost your problem-solving skills
7 note-taking strategies to improve your study skills.

What is abstract thinking? 10 activities to improve your abstract thinking skills

5 examples of cognitive learning theory (and how you can use them)
0 results found.
- Aegis Alpha SA
- We build in public
Building with passion in
- High School
- You don't have any recent items yet.
- You don't have any courses yet.
- You don't have any books yet.
- You don't have any Studylists yet.
- Information
Critical Thinking (1.2, 1.3, 1.5, 1.6)
Critical thinking (phil 102), new jersey city university, recommended for you, students also viewed.
- Quantitative Literacy CH. 10
- Quantitative Literacy Ch.11
- Ch5 HW Quantitative Literacy
- Personal finance Chaper 3 HW
- Personal finance Chaper 4 HW pt1
- Experiment 1 Density lab report
Related documents
- Personal Finance Basics and the Time Value of Money PT1
- Stereochemistry II - This is a required lab report
- Forensics Ch 6 Master Review
- Exp IV Using Freezing-Point Depression to Find Molecular Weight
- Exp VI Rate Determination and Activation of Energy
- Signature Assignment-Financial Literacy
Preview text
Critical thinking (answers to exercises), exercise 1..
- No statement
- Argument. Conclusion: He should avoid her.
- No argument
- Argument. Conclusion: Jesus loves me.
- Argument. Conclusion: Spiderman is a better superhero than Superman.
- Argument. Conclusion: Whether our argument concerns public affairs or some other subject we must know some, if not all, of the facts about the subject on which we are to speak and argue.
- Argument. Conclusion: Don't outlaw guns.
- Argument. Conclusion: If someone says something that offends me, I should have the right to stop that kind of speech.
- Argument. Conclusion: Citizens who so value their "independence" that they will not enroll in a political party are really forfeiting independence.
- Argument. Conclusion: If someone says something that offends me, I cannot and should not try to stop them from speaking.
- Conclusion: Car alarms should be banned.
- Argument. Conclusion: The U. government cannot be trusted when it comes to sending our children to war.
1: Strong family values have been shown to decrease crime rates. Premise: Poverty, political conflict, and deficit spending are all caused by a lack of family values.
2: Any creature that can suffer pain has moral rights. Premise: All animals can suffer pain.
3: Freedom of choice in all things is a basic moral right. Premise: Abortion is no different than scraping off a few cells from one's skin, and a woman certainly has the right to do that.
- Premise: Later I realized that I had completely lost track of time. Premise: I felt as if I was frozen forever.
5: The world's climatologists have predicted that the earth will soon be destroyed by extreme heat and earthquakes. Premise: The world's climatologists are never wrong.
- Premise: Vaughn has admitted that he knows nothing about animals. Premise: The Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals has declared Vaughn a dummy when it comes to animals.
7: The media are reporting that there are suspicions regarding the financial dealings of Governor Spendthrift. Premise: Many people in state government say that they are suspicious of the governor's financial dealings.
Premise: The FBI and CIA say that the Internet is a terrorist's most dangerous weapon. Premise: Terrorists say that their most dangerous weapon is the Internet.
Premise: The Internet has led to the capture of more terrorists than anything else. Premise: The U. Attorney General has asserted that the Internet is the best friend that anti- terrorist teams have.
Premise: Scientific studies have shown that pornography educates people about sexuality. Premise: Societies that use pornography are the most highly educated about sexuality.
Premise: Scientific studies have shown that pornography always misleads people about sexuality. Premise: The more pornography a person uses, the more ignorant he or she is about sexuality.
Premise: All the top TV critics agree that The Sopranos is the greatest series in TV history. Premise: I have compared The Sopranos to all other TV series and found that the show outshines them all.
- Multiple Choice
Course : Critical Thinking (PHIL 102)
University : new jersey city university.

- More from: Critical Thinking PHIL 102 New Jersey City University 7 Documents Go to course

COMMENTS
ANSWERS TO EXERCISES 1. Self-interested thinking 2. Self-interested thinking 3. Self-interested thinking 4. Group pressure (in this case, the we-are-better-than-them type) 5. Group pressure 6. ... Critical Thinking (5.2, 5.3, 5.4) Critical Thinking None. More from: Critical Thinking PHIL 102. New Jersey City University. 7 Documents.
The questions come from the textbook "The Power of Critical Thinking" (sixth edition) by Lewis Vaughn. The answers were reviewed by the professor during class. Skip to document. University; High School. Books; ... Chapter 2 exercises. Only 2.2, 2.3, 2.4, and 2.5. Perceptual Map; Emergent Maths Essay - Grade: A+; Physics II Experiment 3, Hooke's ...
The Power of Critical Thinking: More Answers to the Exercises Contents Chapter Chapter Chapter Chapter Chapter Chapter Chapter Chapter Chapter Chapter Chapter 2 7 12 43 50 56 84 115 131 143 154 Note: Exercises not answered here are found either in the textbook itself or at the companion website: CHAPTER 1 Exercise 2. Critical thinking is ...
2.4 Exercise. Below are 10 entries. Indicate whether they contain reasons and specify what those reasons are. When you are finished, consult this key.Your answers may differ somewhat from those in the key---if so, this is no reason for concern, unless you do not have a reason for thinking you're correct.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Three guidelines to examining a claim or making a choice, The twentieth-century philosopher Bertrand Russell asserts that _____ of an opinion is a sure sign of a lack of reasons to support the opinion: "When there are rational grounds for an opinion, people are content to set them forth and wait for them to operate.
CTQ's are used to to exercise critical thinking by asking and answering questions using who, what, where, when, why, which, and how. During the commitment stage of cognitive and moral development You weigh new information and integrate with what you have previously learned or experienced.
self-corrective manner. It's thinking on purpose! Critical thinking involves mindful communication, problem-solving, and a freedom from bias or egocentric tendency. You can apply critical thinking to any kind of subject, problem, or situation you choose. About This Workbook The activity pages in the Critical Thinking Workbook are meant to be ...
Exercise 4.2 For each of the following premises, fill out the rest of the argument to make it valid in two different ways—modus ponens and modus tollens. *2. If Lino is telling the truth, he will admit to all charges. *5. If religious conflict in Nigeria continues, thousands more will die. *9.
7 Critical Thinking Exercises To Improve Your Critical Thinking Skills. The good news is that by assessing, analyzing, and evaluating our thought processes, we can improve our skills. Critical thinking exercises are key to this improvement. Our critical thinking builds and improves with regular practice, just like a muscle that gets stronger ...
The questions come from the textbook "The Power of Critical Thinking" (sixth edition) by Lewis Vaughn. The answers were reviewed by the professor during class. Skip to document. University; High School. Books; Discovery. ... Chapter 2 exercises. Only 2.2, 2.3, 2.4, and 2.5. Critical Thinking 54% (13) 2. Critical Thinking (5.2, 5.3, 5.4 ...